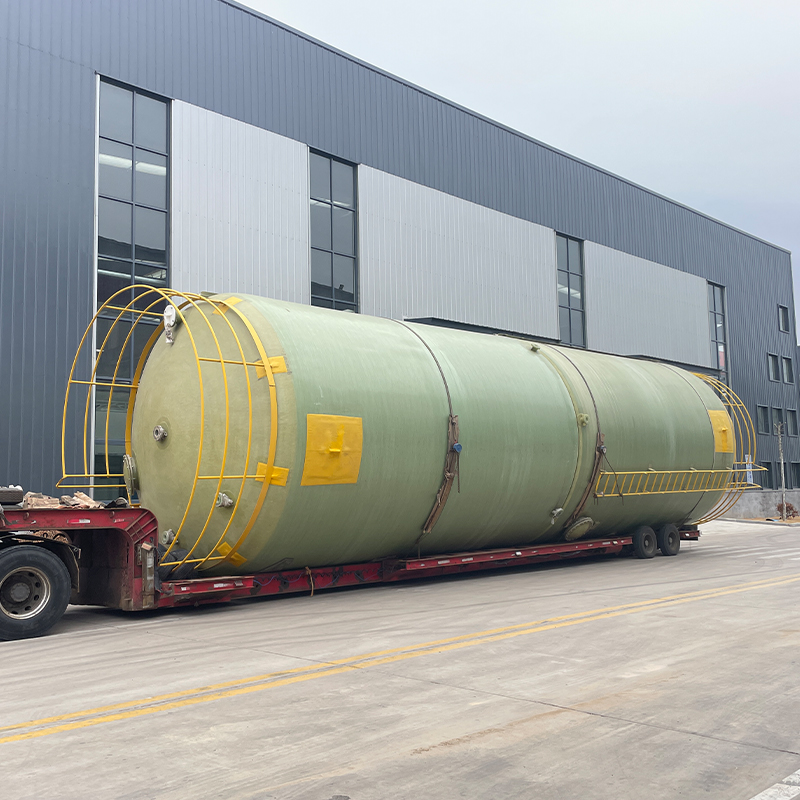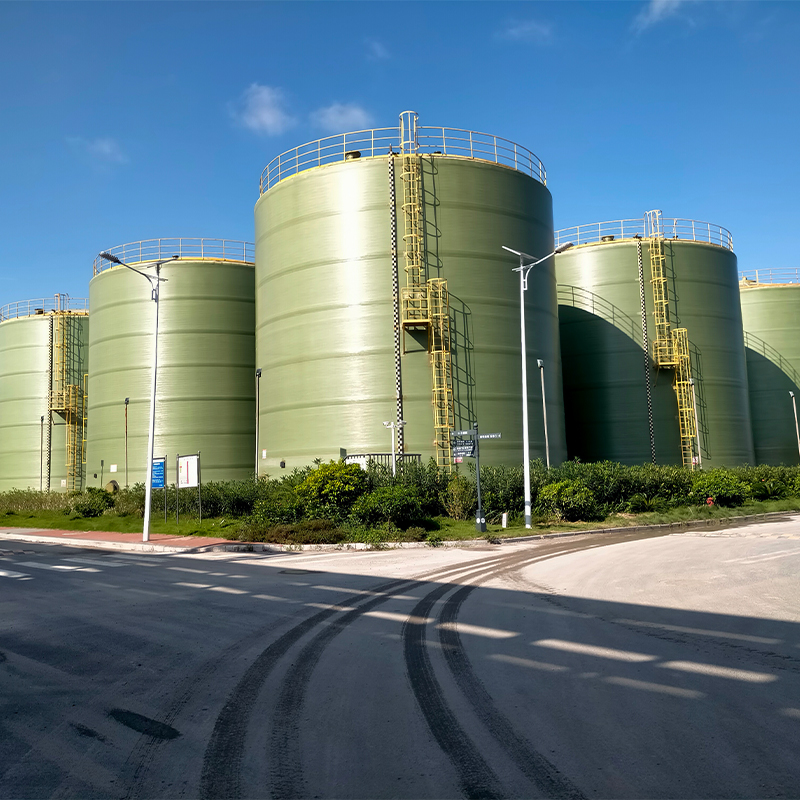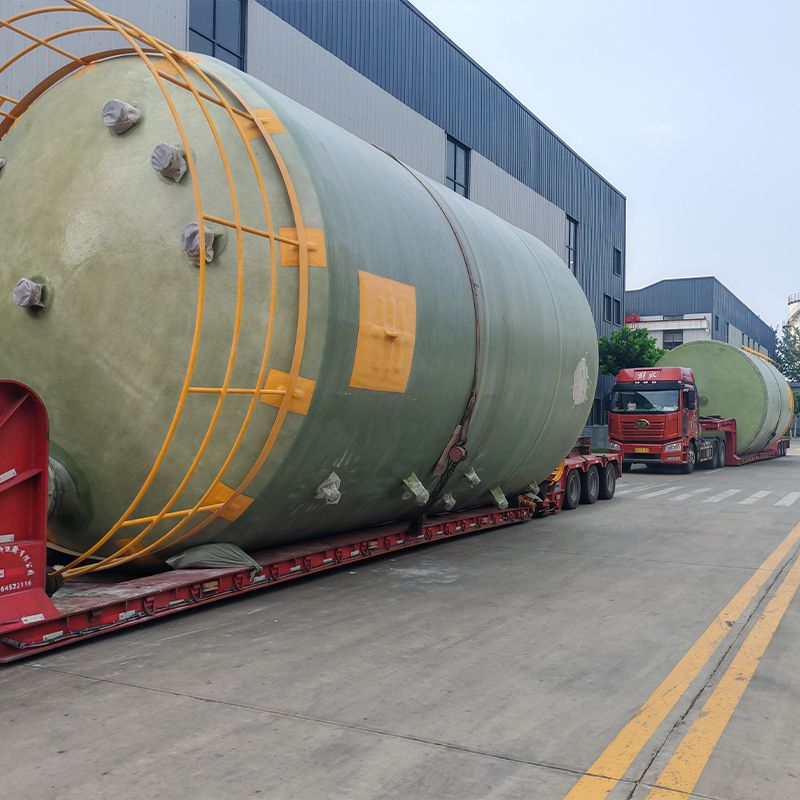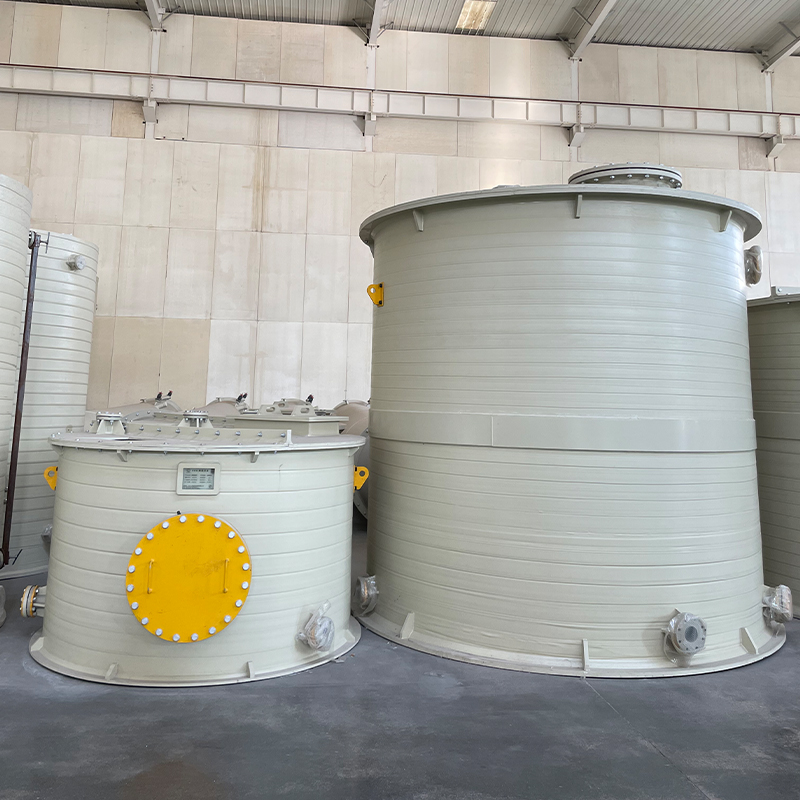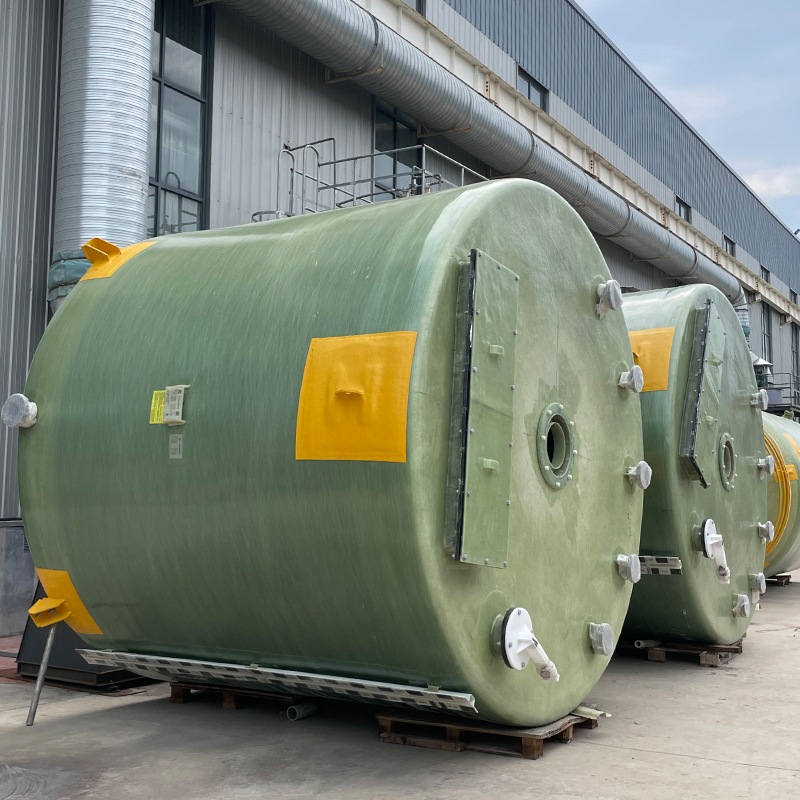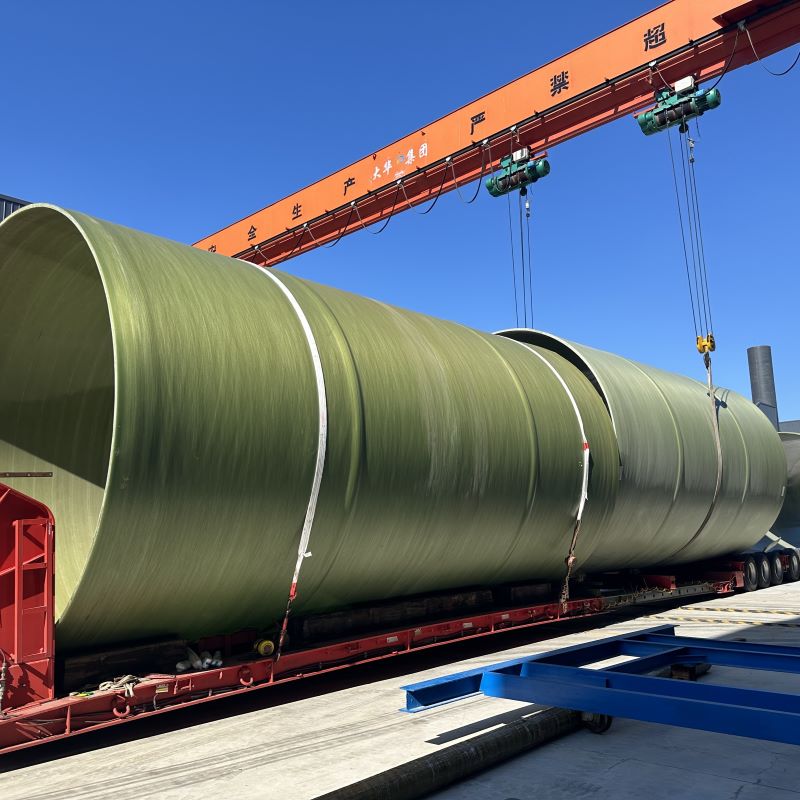
Vertical FRP Hydrochloric Acid Tank
Understanding Vertical FRP Hydrochloric Acid Tanks
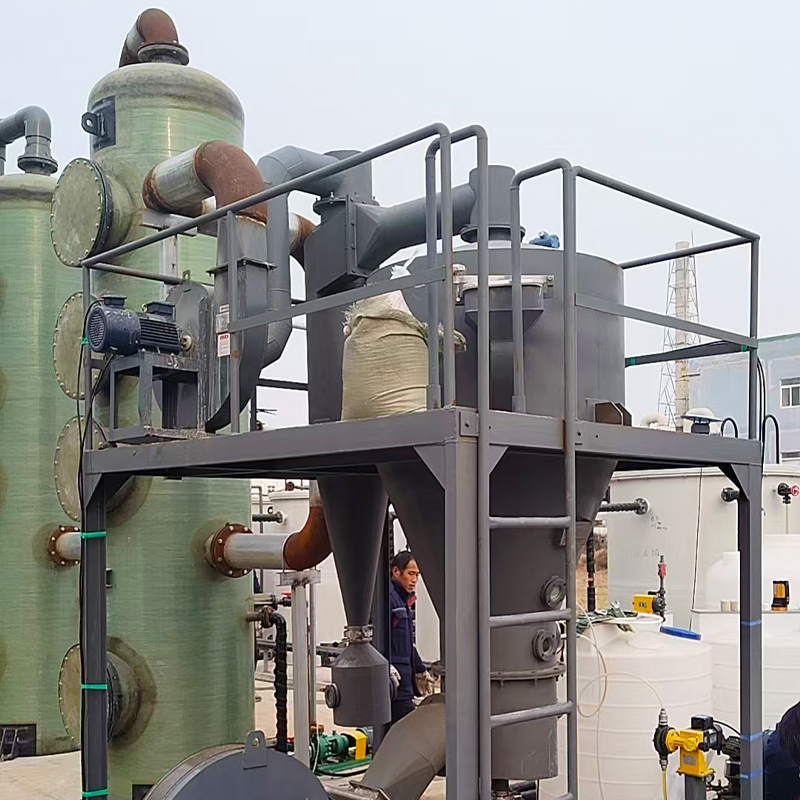
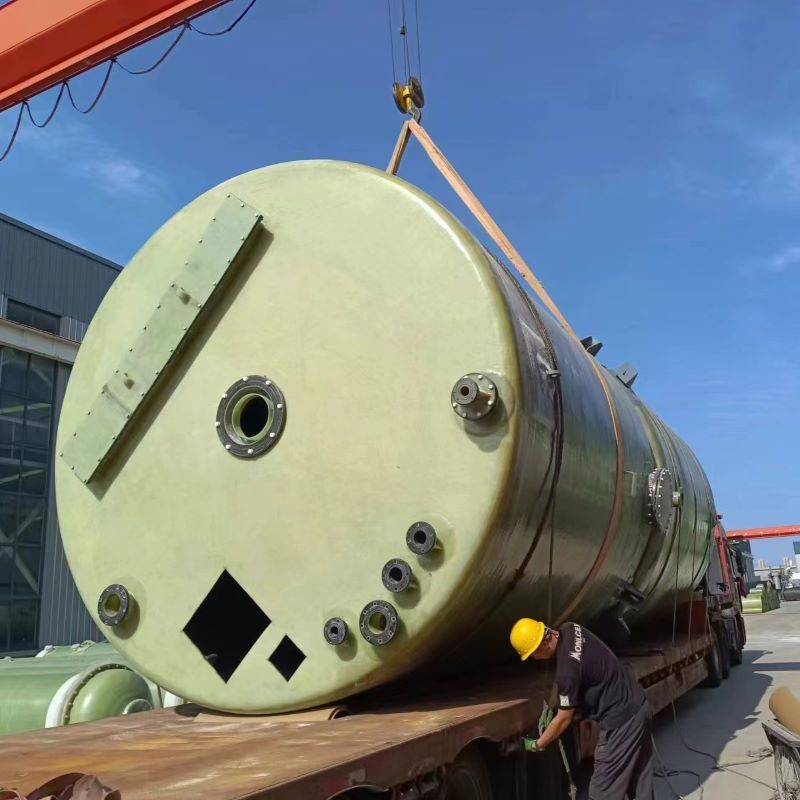
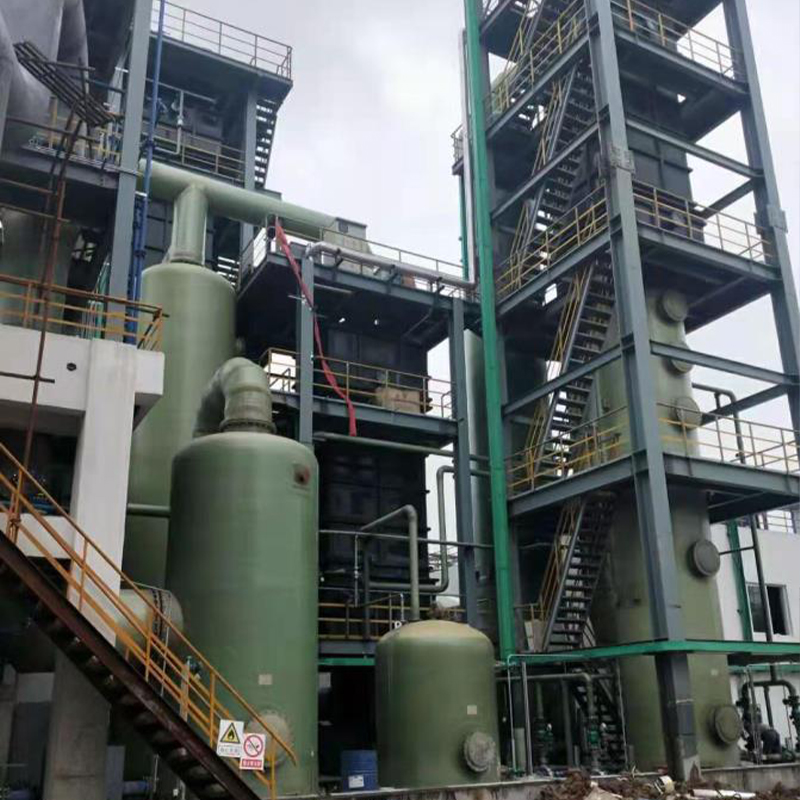
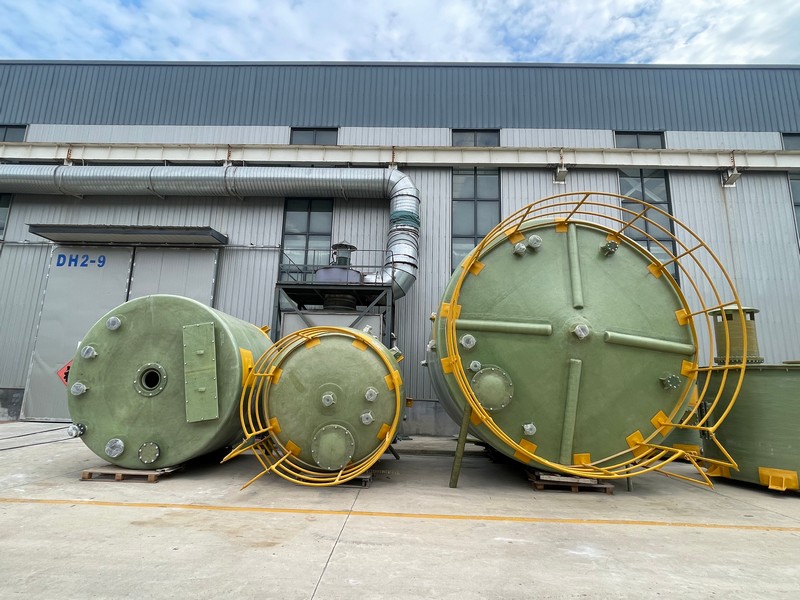
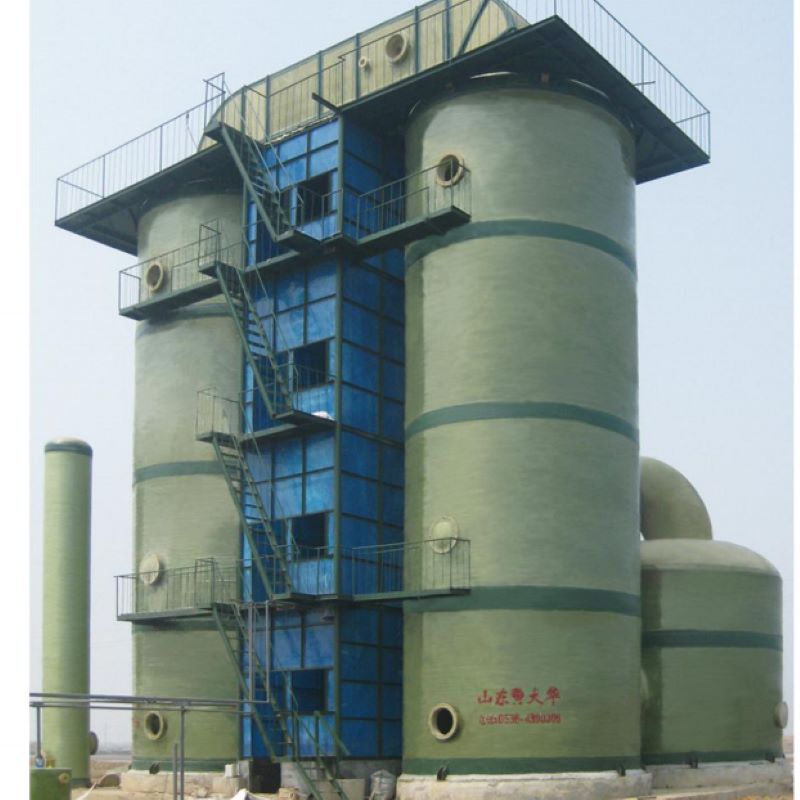
When discussing industrial storage solutions for chemicals, the Vertical FRP Hydrochloric Acid Tank often emerges as a trusted choice. Its advantages are well-known in the sector, yet certain misconceptions persist about its utility and material composition. Let's unravel the complexities through real-world insights.
The Fundamentals of FRP Construction
Fiberglass Reinforced Plastic, or FRP, is celebrated for its corrosion resistance—particularly valuable for storing hydrochloric acid. Unlike metal tanks, which are prone to rust over time, FRP offers a durable solution. But it's not without its intricacies. One might assume simplicity equates to reliability, yet the manufacturing process is crucial. Layers and resin types must be precisely chosen; otherwise, structural integrity might falter.
During a project I was involved with, we encountered unexpected delamination. It was a stark reminder that even the most trusted designs can encounter issues if the composition isn't exact. Collaboration with experienced suppliers made a significant difference, as they helped adjust our approach effectively.
A critical specification is the structural layer setup, including the proper selection of glass fiber mats. The balance between cost and performance often leads to either exceptional durability or premature failure. Therefore, knowing the source and reputation of materials is as vital as the design.
Advantages Over Traditional Materials
The apparent advantages of Vertical FRP Hydrochloric Acid Tanks over traditional materials like steel are numerous. Weight is an often-discussed factor. FRP tanks are significantly lighter, which simplifies installation and reduces foundation requirements. But beyond this, there’s an environmental factor, too—reduced transport emissions due to lighter loads.
Another less obvious advantage lies in the maintenance. Steel tanks frequently demand recoating and inspections to manage corrosion. FRP, despite its lower maintenance demand, still requires periodic checks, focusing on any mechanical damage or resin degradation, which though rare, can happen under extreme conditions.
There's a case that still stands out in my memory where a company overlooked their inspection schedule. A minor abrasion, unnoticed at first, escalated into a costly repair. This emphasized the point; even “low maintenance” shouldn’t imply “no maintenance”.
Design Flexibility and Customization
Vertical FRP tanks excel in adaptability. Customizing for site-specific needs is simpler compared to alternatives. Size, fittings, and support systems can be tailored to the exact specifications needed by an industrial operation. This level of customization offers vast operational flexibility.
I recall a client from the electronics sector needed tanks with specific inlet diameters and unique venting requirements. The adjustments were feasible due to the versatile nature of FRP. The client’s need for modularity in their production line was met with little expenditure on additional infrastructure.
However, the caveat here is ensuring thorough communication with the manufacturer. Custom specifications require precise understanding to avoid costly modifications post-production.
Considerations for Successful Implementation
Integration of FRP tanks isn’t as straightforward as securing a few and bolting them onto an existing setup. It's key to involve multiple departments during the planning phase. Logistics, safety, and engineering teams all play pivotal roles in a seamless adaptation.
One lesson we learned was the value of preliminary mock-ups. Before committing to full-scale installation, testing with scaled prototypes can save considerable resources. This not only verifies practical compatibility but also aids in training personnel in handling any unique operational quirks.
While initial costs and production times are often discussed, long-term savings via reduced maintenance and increased efficiency frequently overshadow these early investments.
Potential Drawbacks and Mitigation
No solution is without drawbacks, and FRP tanks present potential issues primarily related to mechanical impacts. Because they aren't as rigid as steel, unexpected stress might lead to material fatigue over time. Identifying suitable siting and providing appropriate shielding can effectively mitigate these risks.
There was an incident involving moving equipment on a busy site that led to unintended tank damage. This situation stressed the importance of integrating risk management into storage planning—something often sidelined during the rush of operational demands.
Lastly, the correct instructional training ensures hazard awareness among employees. If personnel understand the unique properties of FRP tanks, incidents can be minimized, and long-term performance assured.
Conclusion: Delving Deeper Into Decisions
Every decision concerning industrial storage is significant, especially in sectors involving hazardous substances like hydrochloric acid. Vertical FRP tanks bring numerous advantages, yet they require careful consideration and informed practices to maximize their potential.
As the industry evolves, continuous learning and adaptation will underscore the shift toward these modern solutions. Sites like our website provide a window into how companies are harnessing these technologies. And as we keep sharing experiences, we only strengthen the community’s knowledge and resilience.
Соответствующая продукция
Соответствующая продукция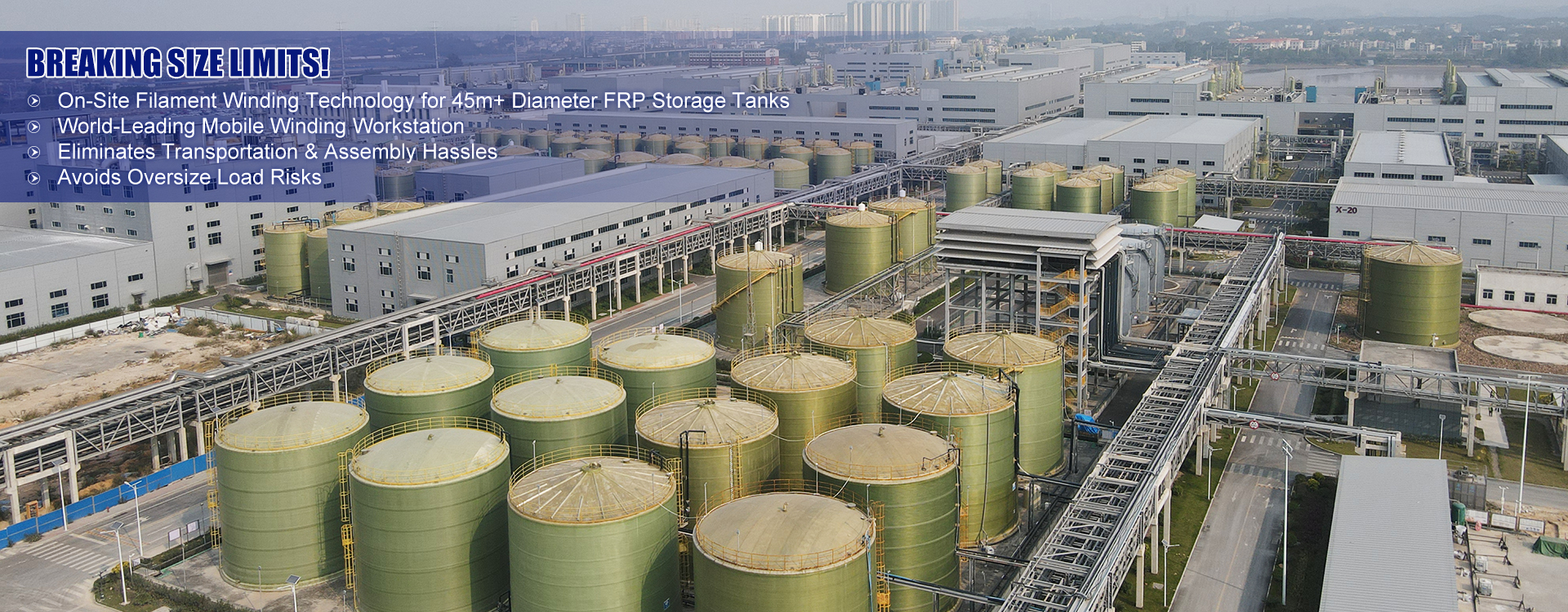
Самые продаваемые продукты
Самые продаваемые продуктыСвязанный поиск
Связанный поиск- Best FRP Process Pipes exit
- high quality frp tank for water treatment factory
- China Horizontal FRP Storage Tank Manufacturer
- China PPH Scrubber Tower supplier
- Best Chemical-Resistant FRP Storage Vessel exit
- high quality rooftop evaporative cooler
- OEM PPH Agitator tank Manufacturer
- frp storage tank manufacturers Manufacturer
- Best updraft evaporative cooler price
- Best High-Efficiency Energy-Saving Closed-Circuit Cooling Tower factory























