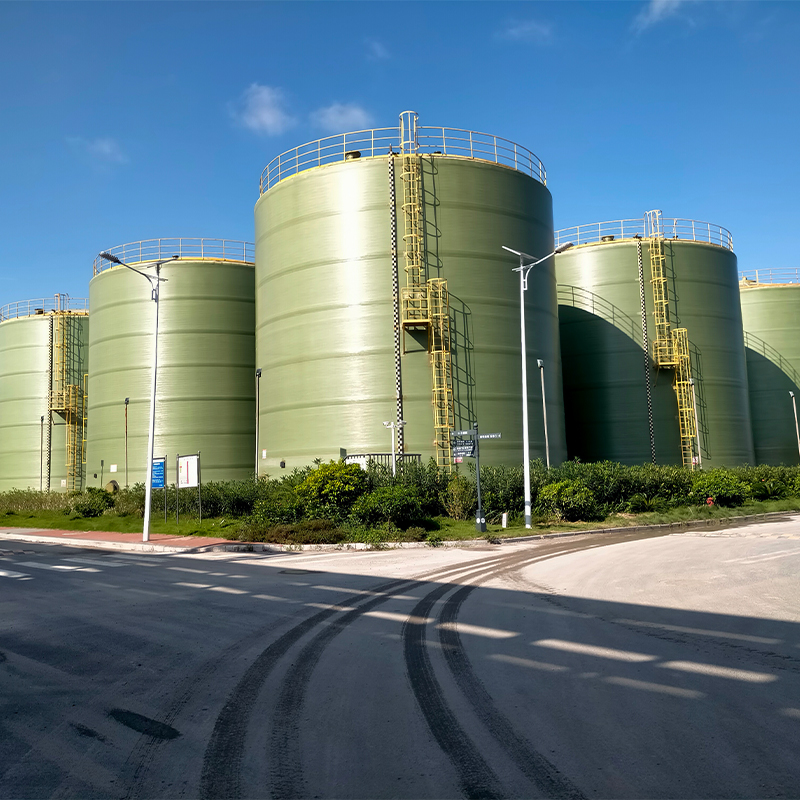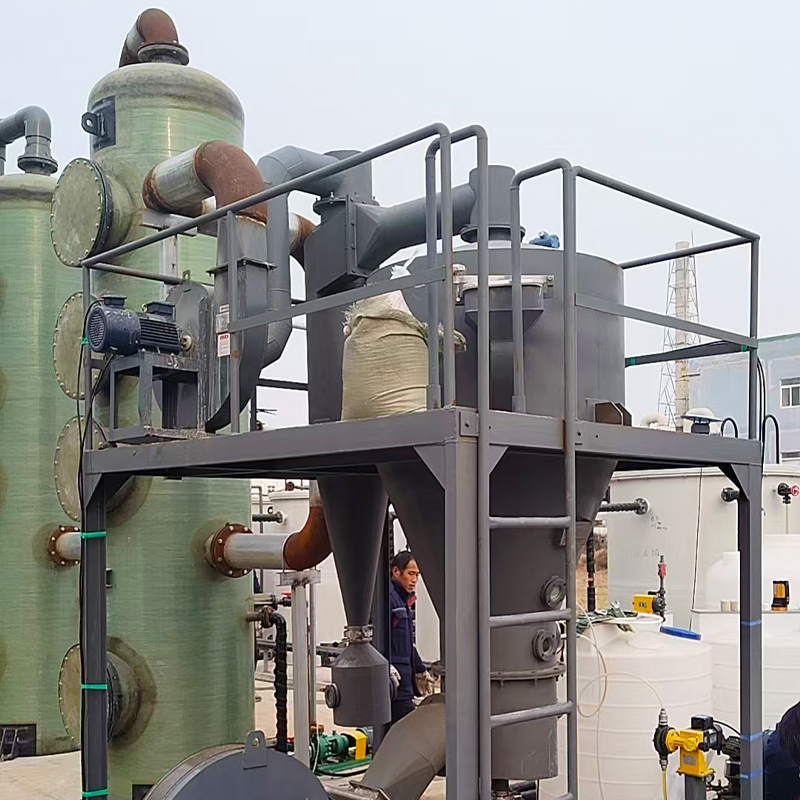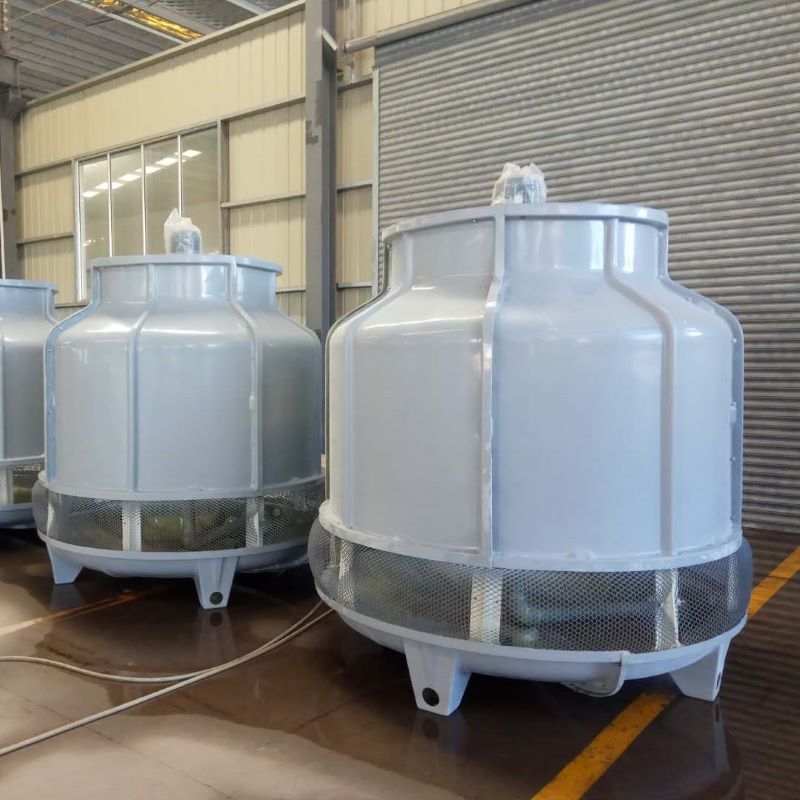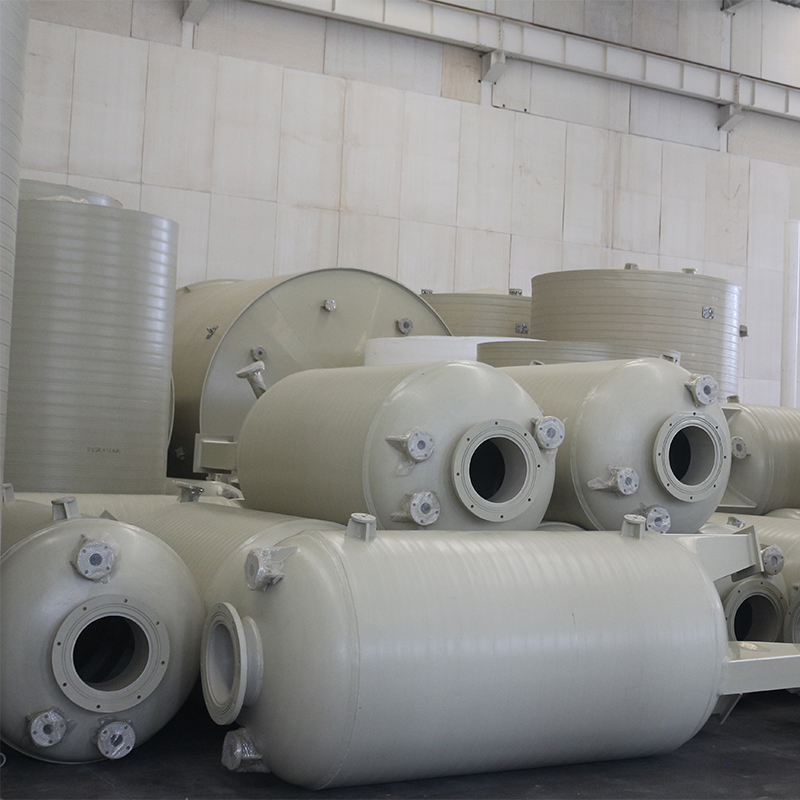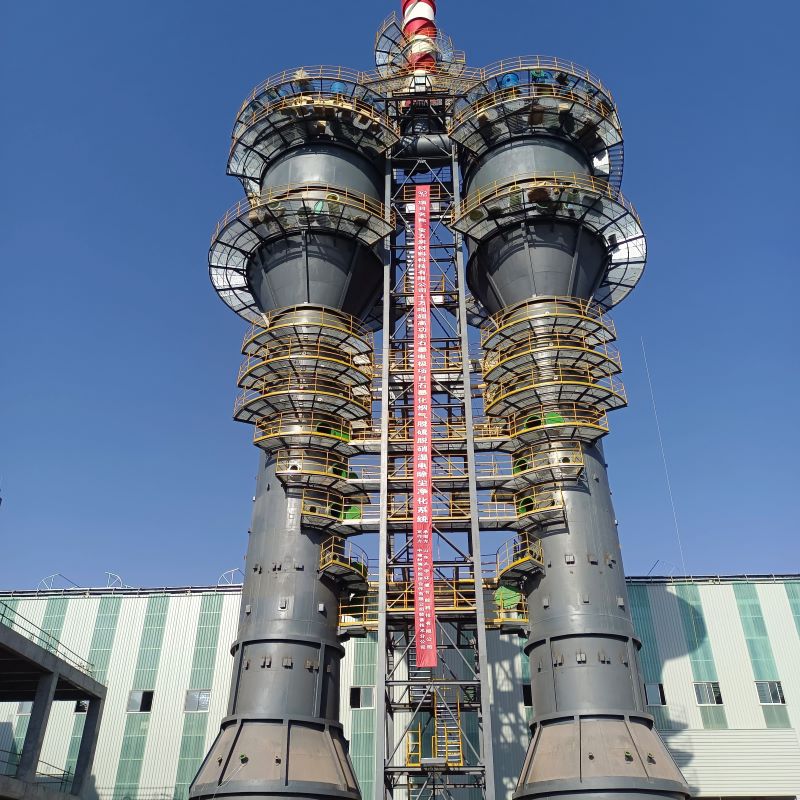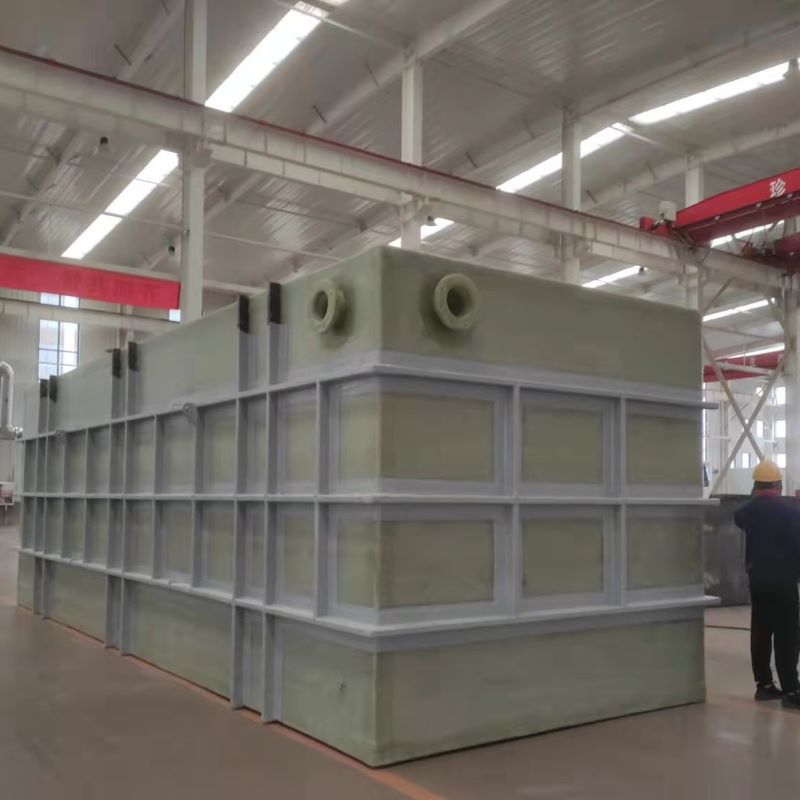
PP Storage Tank
The Practical Insights into PP Storage Tanks
Understanding Polypropylene (PP) storage tanks can spell the difference between a successful chemical storage solution and a potentially costly error. These durable, chemical-resistant tanks are pivotal in various industries. Yet, the nuances in their application often go unnoticed until an issue arises.
Recognizing the Essentials of PP Storage Tanks
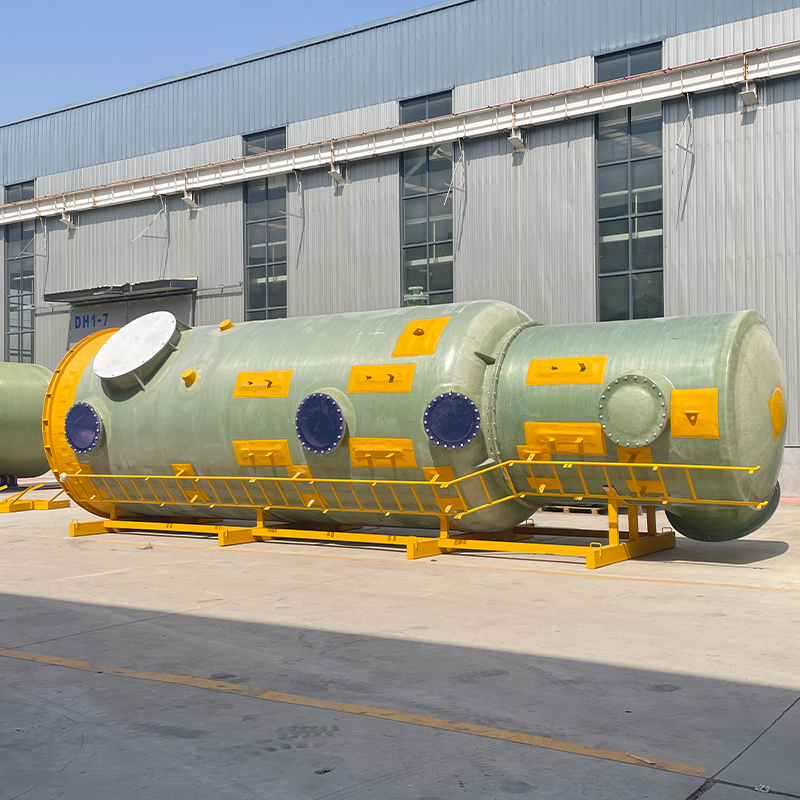
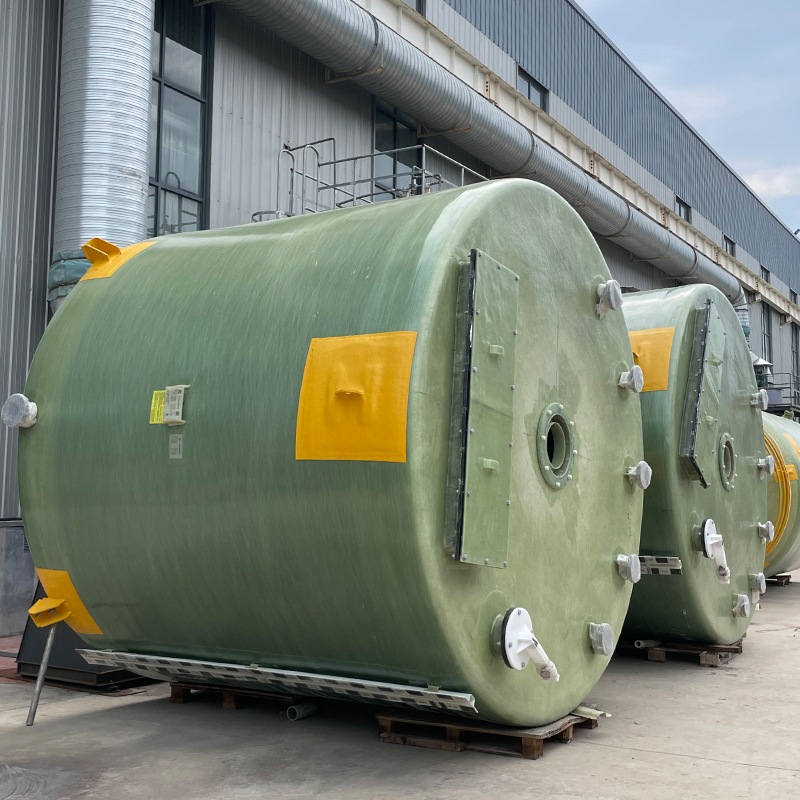
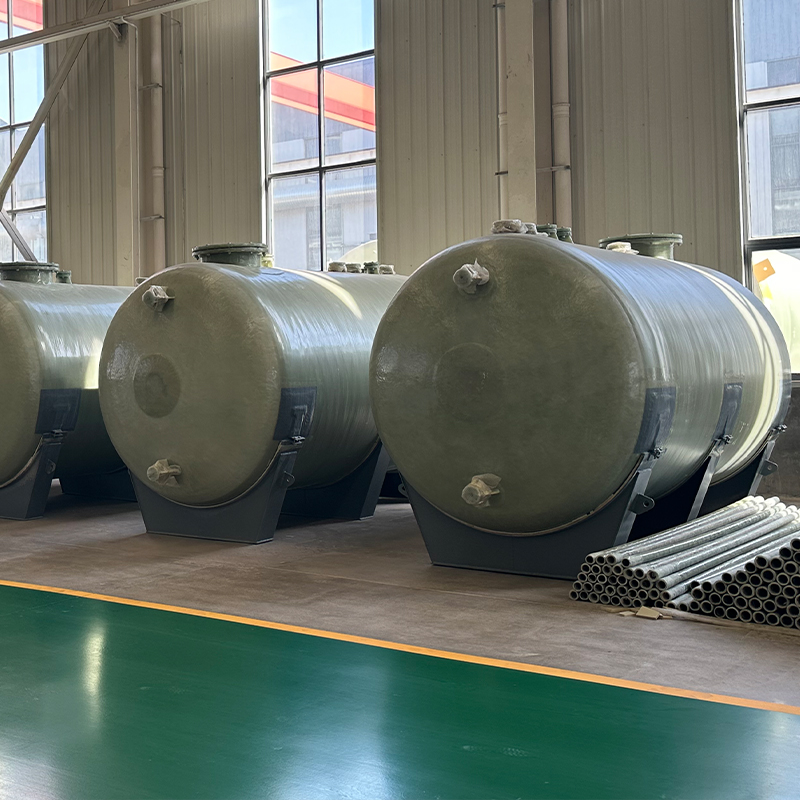
At first glance, polypropylene might seem like just another type of plastic, but in the realm of storage tanks, its significance cannot be understated. PP tanks offer excellent resistance to a wide range of chemicals, making them ideal for industries like pharmaceuticals and wastewater management. I recall a project where a poorly chosen tank material led to severe corrosion issues; it was an expensive lesson that reinforced the value of using PP storage tanks when dealing with aggressive chemicals.
What often surprises newcomers is the material’s temperature tolerance. While PP is fantastic in many respects, you have to be mindful of its limitations when exposed to high heat. There was an incident with a client trying to store high-temperature liquids in PP tanks without proper insulation. Unfortunately, it resulted in deformation of the tanks.
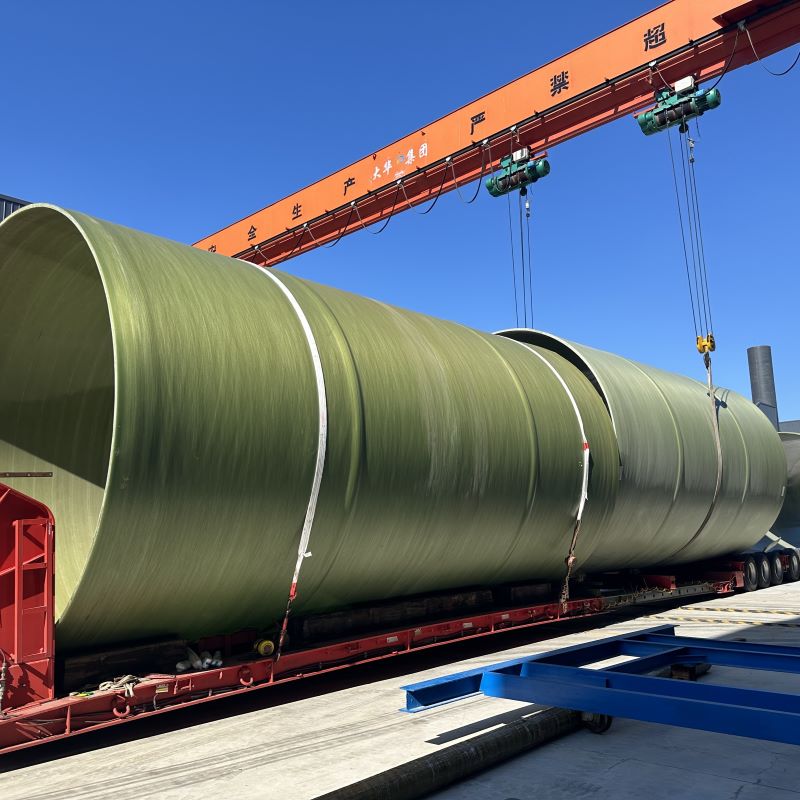
The weight advantage of PP tanks is another aspect that appeals to many. They are much lighter compared to steel or fiberglass alternatives, simplifying transport and installation—but be wary of using them in applications where structural rigidity is a primary concern. This balance of benefits and drawbacks makes understanding the specific application crucial.
Installation Nuances and Considerations
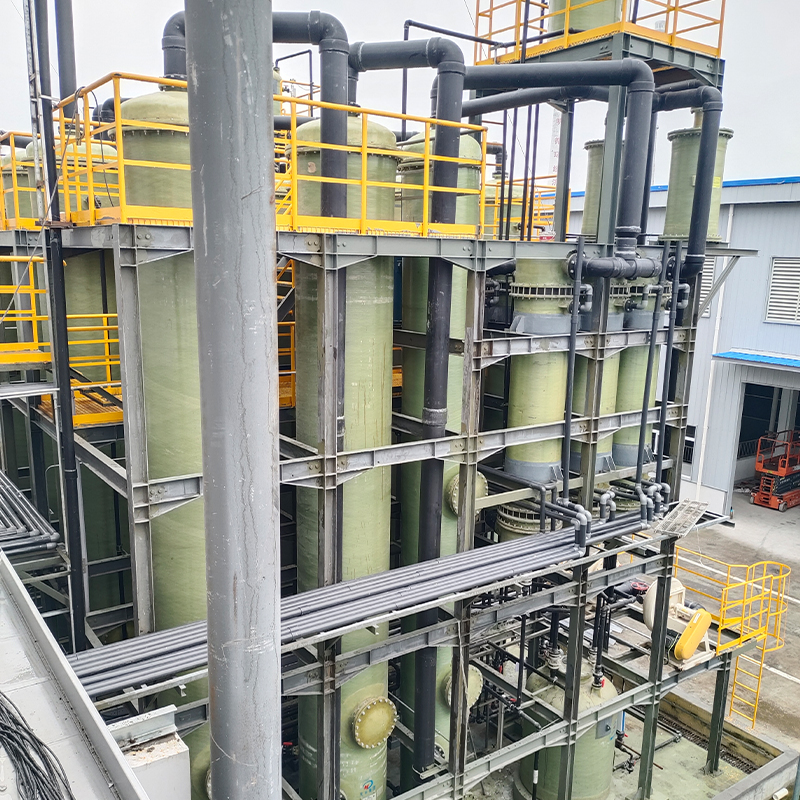
Installation practices can make or break the efficacy of PP storage tanks. It’s crucial to ensure that tanks are placed on a level surface. Any deviation can lead to stress points, especially when the tanks are filled. I’ve seen installations where meticulous leveling was ignored, leading to premature fatigue cracks.
An important factor in installation is ensuring that the tanks are properly vented, particularly when dealing with volatile substances. PP tanks, while sturdy, can bulge or even crack under pressure if improper venting occurs. Incorporating pressure release systems is a common strategy that I've seen work effectively.
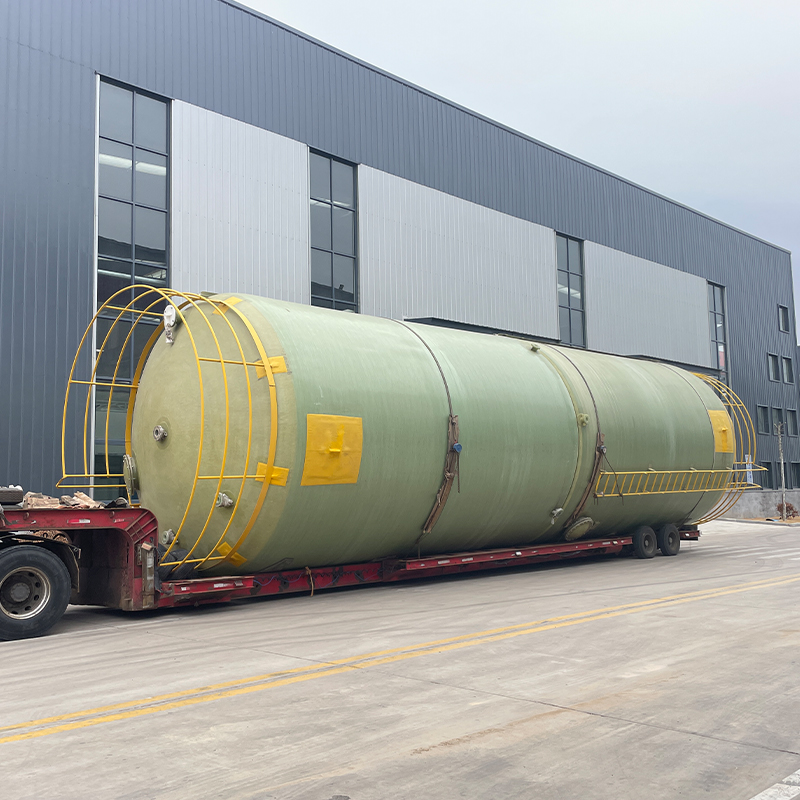
Another installation tip often overlooked is the use of flexible connections for inlet and outlet piping. During a maintenance check, I discovered a rigid connection causing undue stress on the tank fittings; switching to flexible connections solved the problem immediately.
Maintenance and Longevity Insights
Regular maintenance of PP storage tanks can extend their longevity significantly. Inspections should focus on checking for chemical compatibility, leaks, and deformations. I’ve found that maintaining a routine inspection schedule, as simple as it sounds, can be a game-changer.
A colleague once underscored the importance of cleaning tanks thoroughly between different chemical uses to prevent unexpected reactions. It’s a practice many neglect, but it can prevent costly damage.
While PP is inherently resistant to many chemicals, exposure to UV light over time can degrade the material. Installing tanks in shaded areas or using UV-protective coatings can greatly enhance the lifespan of PP storage tanks.
Application-Specific Recommendations
The choice of PP for storage often depends on the sector. In the chemical industry, for instance, it’s vital to cross-reference compatibility charts with the chemicals in question. During a consultancy, we identified materials that were seemingly benign but had long-term adverse effects on the PP tanks used.
For agricultural applications, the ease of transporting PP tanks often trumps other considerations. Farmers frequently appreciate their lightweight nature. However, ensuring the tanks are secured and anchored is essential to prevent tipping, especially in windy conditions.
In wastewater management, corrosion resistance is the key feature. Here, PP tanks often outperform other materials. I recall instances where switching to PP resolved pipeline contamination issues that plagued a facility reliant on other types of tanks.
Future Trends and Developments
With the increasing emphasis on sustainable materials, PP tanks are likely to see enhancements that could improve their environmental footprint. Innovations in polymer science are paving the way for more recycled materials in manufacturing.
Companies are exploring hybrid tanks that combine PP with other materials to enhance its temperature and pressure resilience without sacrificing chemical compatibility. I’m curious to see how these innovations will play out in real-world applications.
Looking forward, it’s intriguing to consider how these advancements will alter industry standards and practices, potentially opening up new applications for PP storage tanks across various sectors.
For comprehensive solutions and products, visit SDDAHUA Group, which provides a wide range of tailored storage solutions suited for diverse industrial needs.
Соответствующая продукция
Соответствующая продукция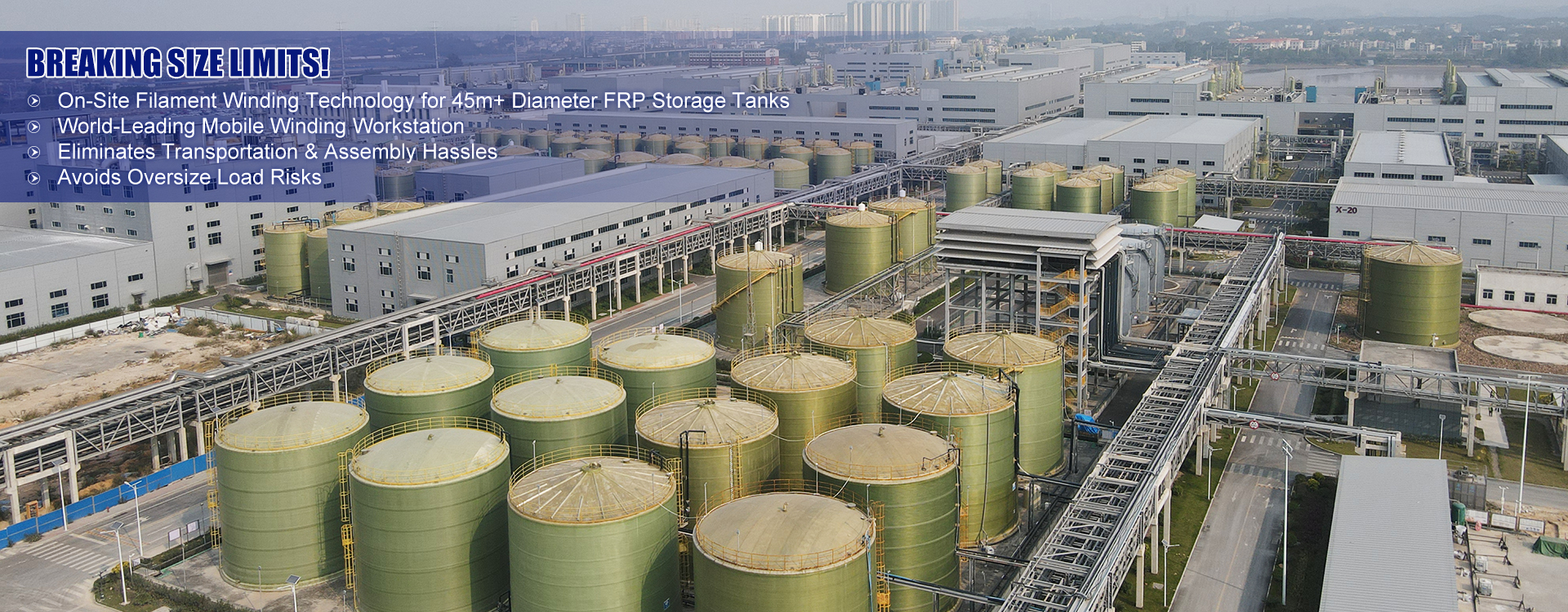
Самые продаваемые продукты
Самые продаваемые продуктыСвязанный поиск
Связанный поиск- Best Hydrochloric Acid Treatment Unit for Potassium Sulfate exit
- high quality warehouse evaporative cooler factory
- China PPH Absorption Column factory
- China best outdoor evaporative cooler
- OEM FRP Chimney exit
- high quality FRP Composite Vessel Manufacturer factory
- China PPH tower supplier
- Best evaporative cooler window unit exit
- OEM PPH Mixing Tank Manufacturer
- FRP Process Tank factory























