China side draft evaporative cooler
Understanding China Side Draft Evaporative Coolers: An Insider’s Perspective
In regions with dry climates, the use of evaporative coolers offers a practical and efficient solution for temperature control. Specifically, the China side draft evaporative cooler is gaining attention for its unique design and functionality. But what makes it stand out, and are there any pitfalls professionals need to be wary of when adopting this technology?
Exploring the Side Draft Design
The term 'side draft' essentially refers to the air intake direction of the cooler. Unlike the down draft or up draft models, side draft coolers pull air from the side, making installation a bit more flexible depending on the available space. This design can fit well in certain architectural layouts that limit vertical space or require specific airflow patterns.
From my experience, one challenge with side draft coolers is ensuring there's enough surrounding space for efficient air intake. A friend once had a unit installed too close to a wall, significantly affecting its performance. Hence, proper placement is crucial.
Companies like those on this site offer a range of products that can adapt to different building requirements, which is beneficial for customization but sometimes overwhelming in choice.
Efficiency and Performance
When it comes to cooling efficiency, the China side draft models often boast impressive statistics. They frequently utilize high-quality pad materials that enhance evaporation and cooling efficacy. Despite such promising figures, real-world performance can vary. Factors like local climate conditions, unit maintenance, and installation quality all play a part.
During a project in Xi'an, we encountered inconsistent cooling outcomes due to improper maintenance schedules. Keeping the pads clean and ensuring regular water supply were critical steps we, unfortunately, learned the hard way.
Nevertheless, maintaining these units isn't vastly complex, and they tend to have fewer moving parts compared to traditional air conditioning systems, reducing the likelihood of mechanical failures.
Cost Considerations
In terms of cost, the initial investment for a China side draft evaporative cooler can be quite appealing. They're generally more affordable than traditional air conditioning systems, both in upfront costs and operational expenses. This cost-effectiveness makes them an attractive option for many businesses looking to maximize budget efficiency.
However, the cost of water should be considered. The efficiency of these units strongly ties to their ability to evaporate water continually. In regions where water resources are limited, this could pose a monetary challenge.
Some manufacturers provide models with water conservation features, but it's essential to weigh these benefits against their higher purchase price.
Environmental Impact
From an environmental standpoint, evaporative coolers have a lighter footprint compared to refrigerant-based systems. No harmful chemicals are used in their operation, which aligns well with sustainable practices. This aspect is increasingly vital as businesses seek to align with global environmental targets.
In one factory setup I was involved in, the shift to side draft evaporative coolers helped meet corporate sustainability goals while maintaining worker comfort. The ability to use renewable energy sources to power these units further enhances their green credentials.
Yet, the reliance on water needs careful management to ensure sustainability, especially in water-scarce areas where the environmental benefits might otherwise be offset.
Integration with Smart Technologies
The integration of smart technologies in industrial equipment, including evaporative coolers, has become increasingly common. This technology enables remote monitoring and efficiency optimization, allowing for better resource management.
Manufacturers featured on platforms like this are incorporating IoT capabilities into their systems. Such advancements can revolutionize maintenance and efficiency tracking, though they also come at an extra cost.
On a practical note, ensuring your facility network can support these technologies is critical. A client once had to overhaul their entire network setup to accommodate smart operations, a costly and disruptive process that should have been planned from the start.
Соответствующая продукция
Соответствующая продукция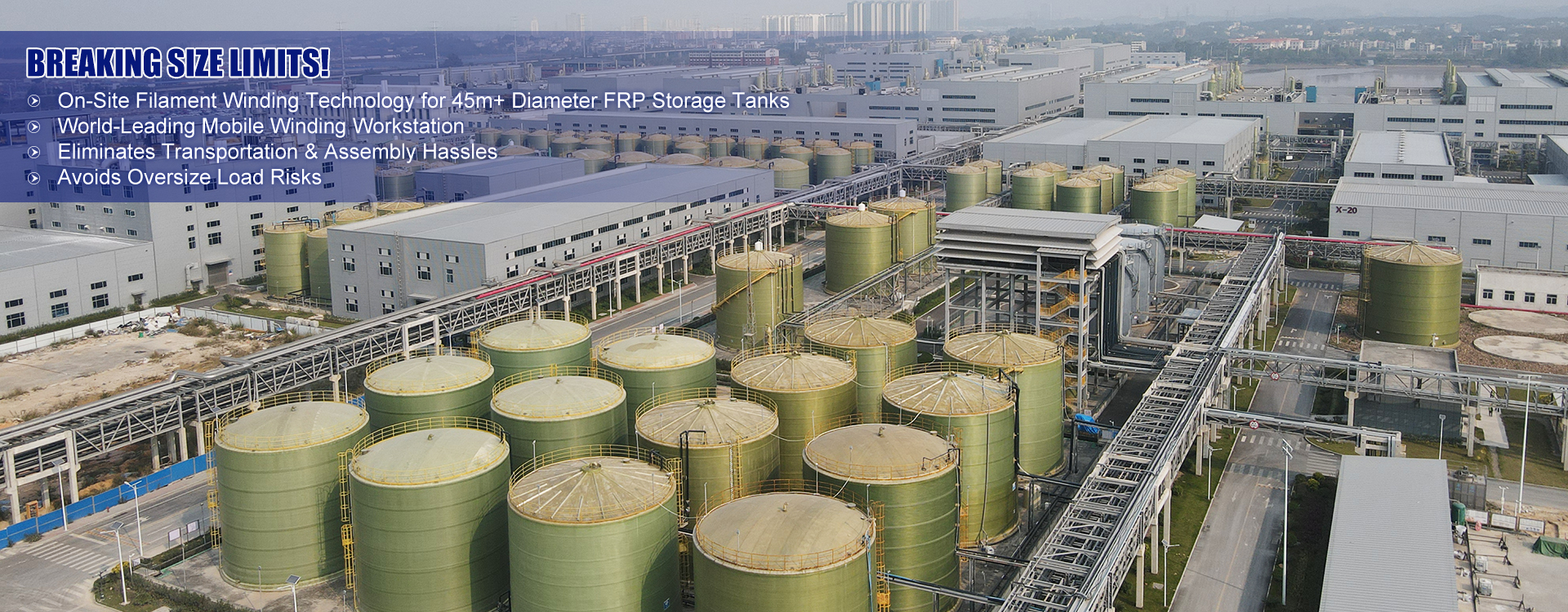
Самые продаваемые продукты
Самые продаваемые продуктыСвязанный поиск
Связанный поиск- high quality central evaporative cooler factory
- high quality PP Spray Tower price
- Best Air-Cooled Heat Exchanger product
- OEM FRP Composite Storage Tank product
- Best Horizontal FRP Tank Manufacturer factory
- Best Vertical FRP Hydrochloric Acid Tank price
- China FRP pipes
- OEM Evaporative-Condenser factory
- underground frp tanks factory
- Heat Exchange Equipment factory


























