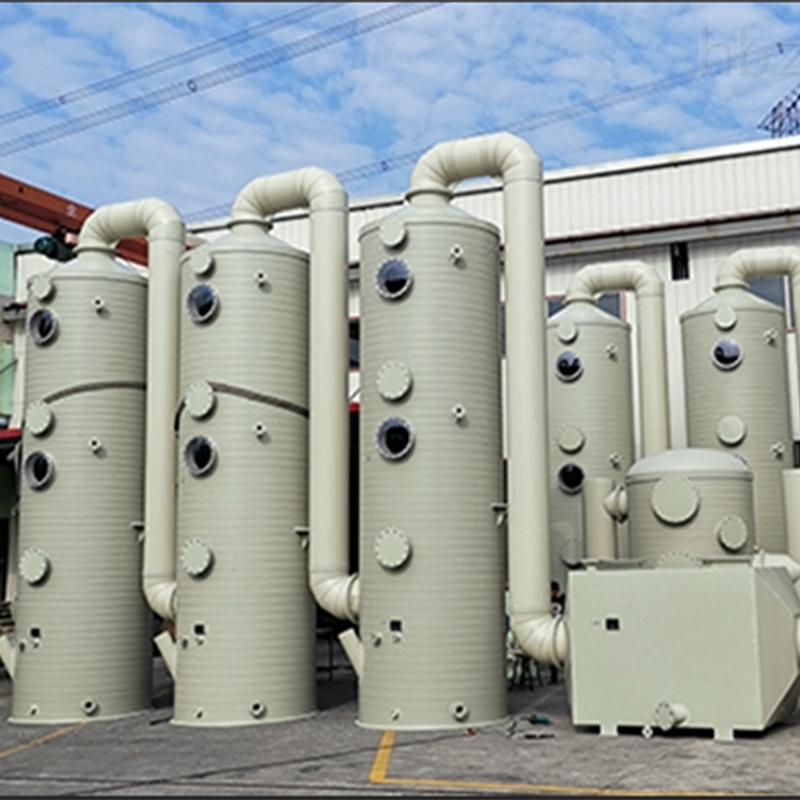
China PPH Spray Tower
Understanding the Dynamics of China's PPH Spray Tower Technologies
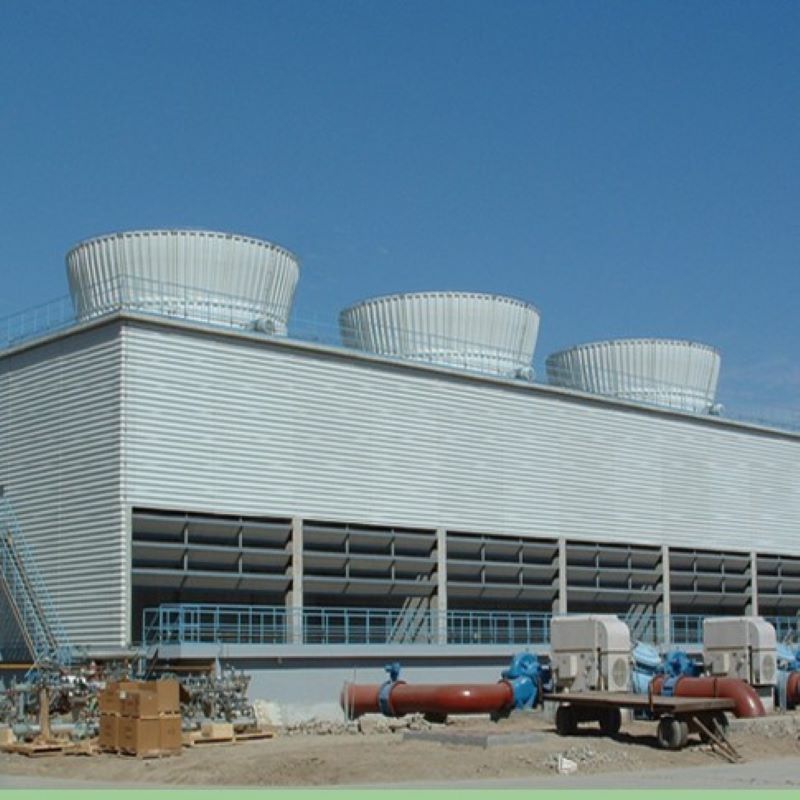
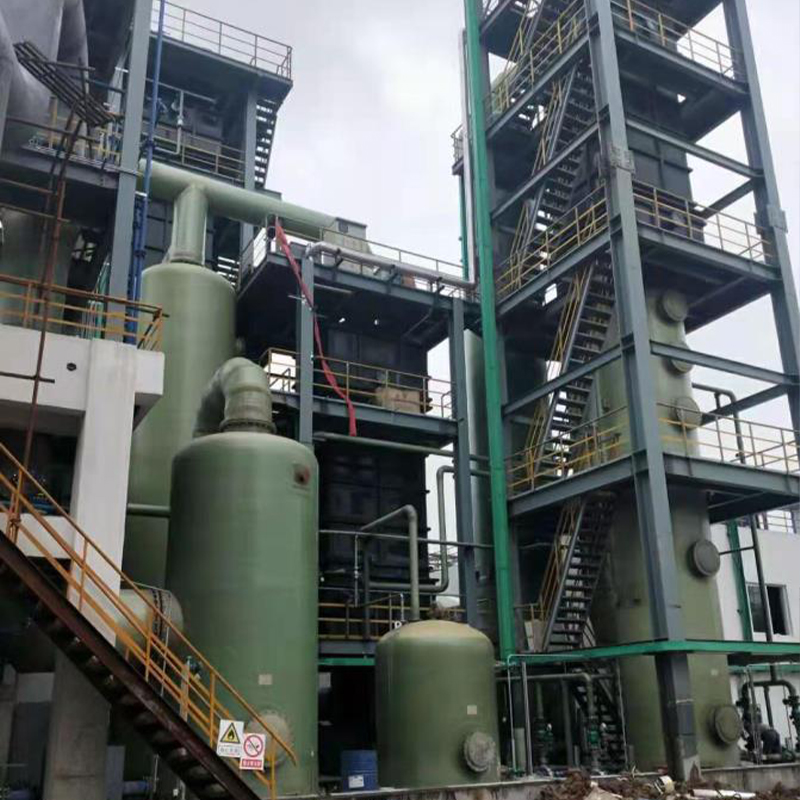
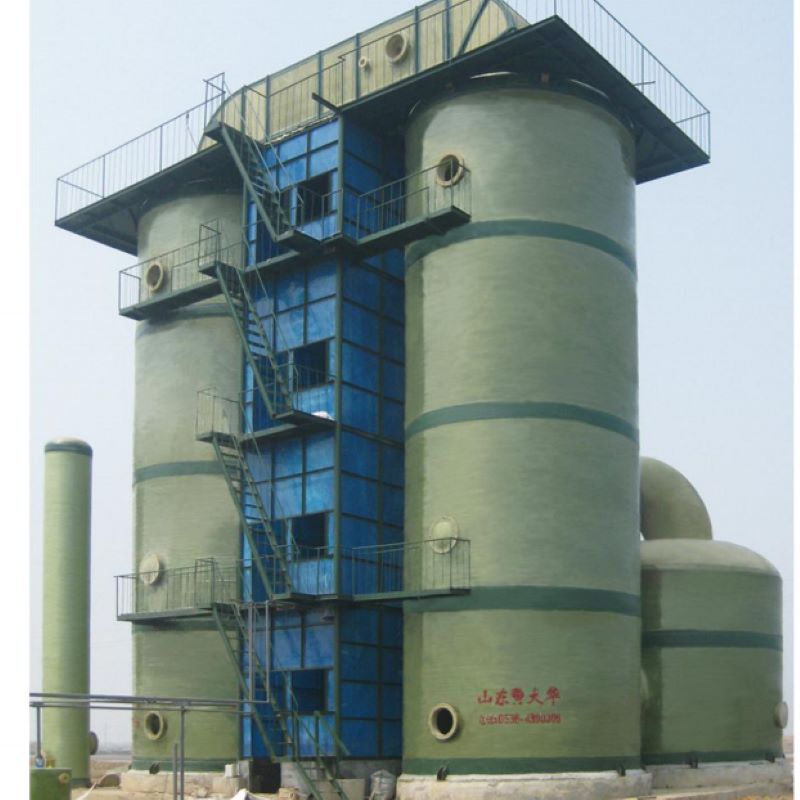
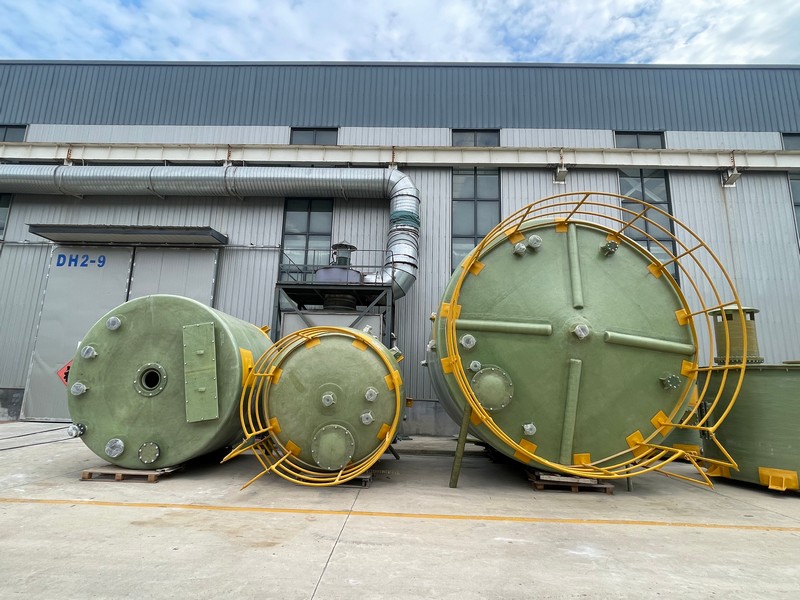
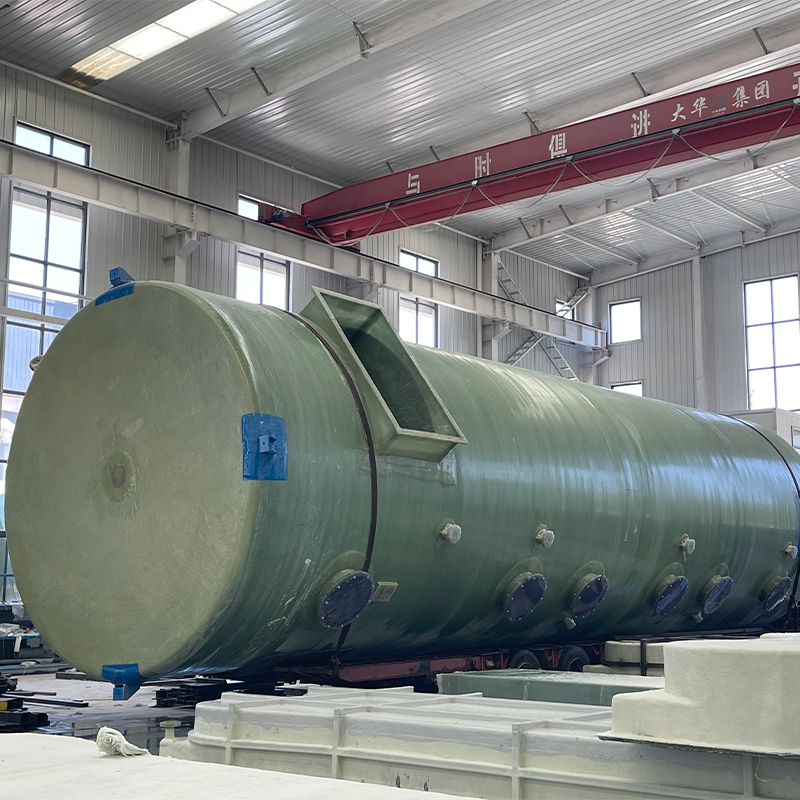
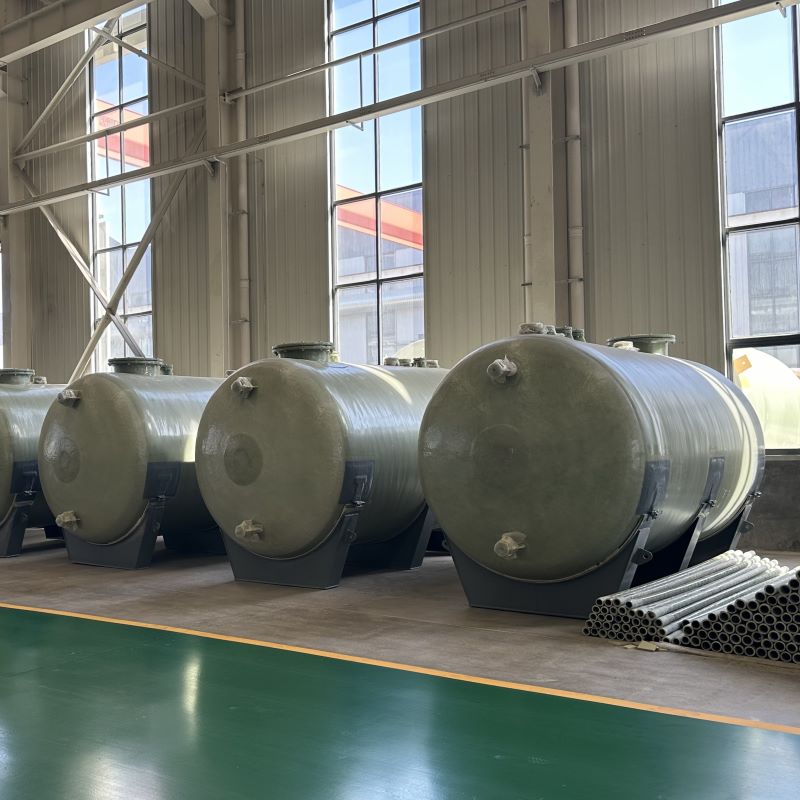
If you’ve ever delved into the realm of industrial exhaust treatment, the term PPH Spray Tower from China has probably echoed through your discussions. It’s a fascinating piece of engineering that promises efficiency and durability, yet there’s more beneath the surface than its robust exterior suggests.
The Evolution of PPH Spray Towers in China
China's journey with PPH Spray Tower systems began as an ambitious stride towards improving industrial air quality. Initially, these towers were conceived primarily to manage and mitigate harmful emissions released in heavy industrial processes. The evolution, however, has reflected a blend of technological innovation and practical necessity.
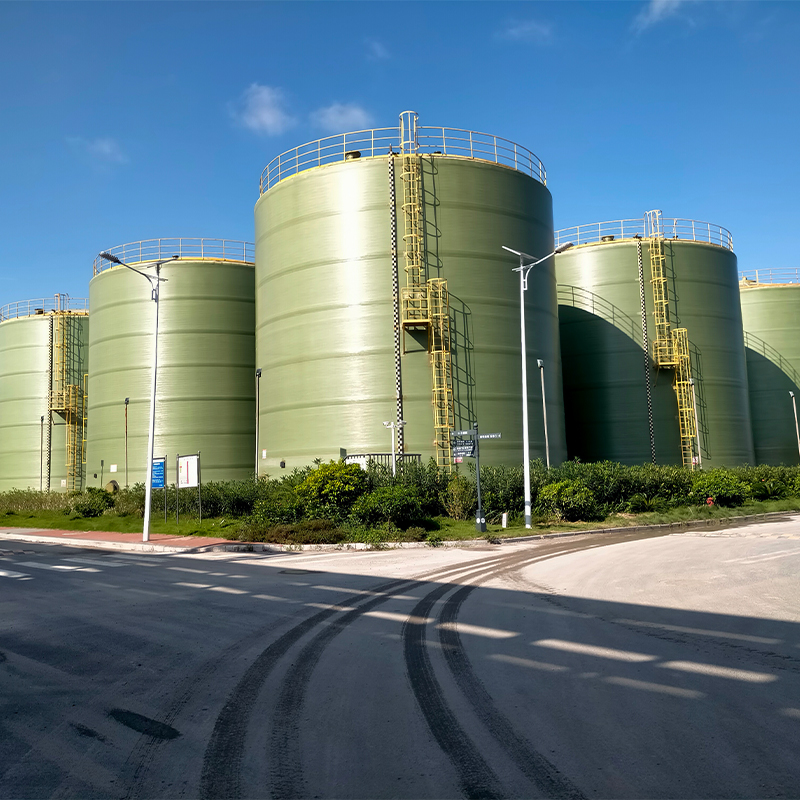
In the early days, the challenge was about scaling production without compromising on quality. Many manufacturers experimented with different materials, but PPH (Polypropylene Homopolymer) emerged as a leading choice due to its chemical resistance and structural integrity. This material could withstand the hostile conditions typically associated with industrial emissions, such as high temperatures and corrosive substances.
One might argue that quality control was initially a stumbling block, but over time, with increased collaborations and technological exchanges between companies, including international ventures, the standards have risen dramatically. From what I've observed, firms have particularly focused on enhancing the longevity and maintenance efficiency of these towers.
Challenges in Implementation
While the benefits are clear, implementing a PPH Spray Tower isn't without its headaches. In my consultancy work, I've seen numerous cases where the configuration of the spray nozzles came under scrutiny. The nozzles are key, but getting them right requires a delicate balance—they need to ensure maximal contact between air and scrubbing liquid without hampering the system's operations.
In some instances, improper nozzle setups led to blockages or suboptimal performance. Fixing these issues often demands on-site adjustments, highlighting the need for skilled technicians who can quickly diagnose and rectify these nuances. Moreover, there's the constant battle against wear and tear, a battle that the robust properties of PPH should ideally mitigate, yet vigilance is always required.
An interesting case was with a medium-scale enterprise that underestimated the tower's drainage system needs. The oversight led to an accumulation of residues, prompting an unexpected halt in operations. That experience was a stark reminder of the importance of comprehensive initial planning and testing.
Customization and Flexibility
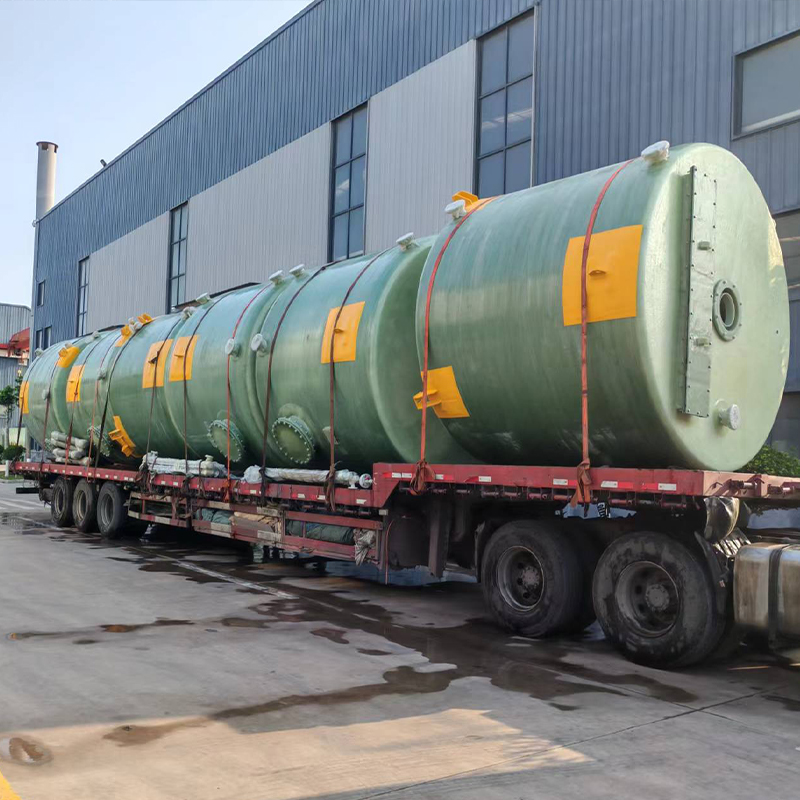
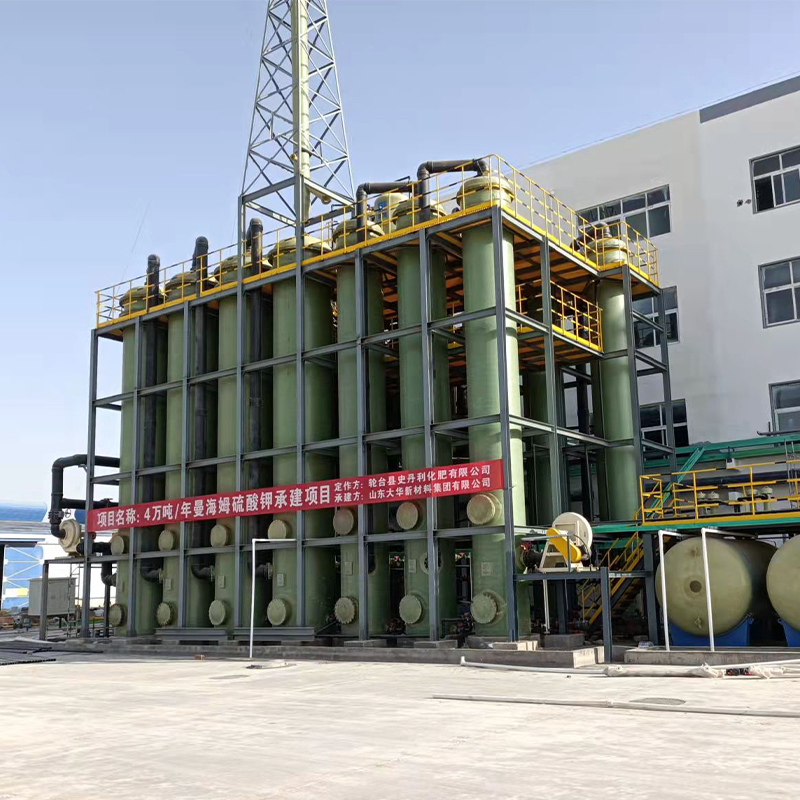
The versatility of China’s PPH Spray Tower is one of its strongest selling points. What I've noticed, especially with companies like Shandong Dahuagroup, is a keen focus on tailor-made solutions. They often customize the design to fit specific client needs, which can range from chemical manufacturing to waste management industries.
Take the instance of a client in the textile industry—they needed a solution that could handle volatile organic compounds effectively. The modular approach allowed for additional features like heat recovery sections, ensuring not only compliance but also cost-efficiency in terms of energy use.
Flexibility extends beyond physical customization. Many companies now offer modular training for operating personnel, emphasizing hands-on experience with the equipment. After all, the tower’s efficiency largely hinges on how well it's managed day-to-day.
Cost Considerations
Discussing costs can be tricky. The initial purchase and setup of a PPH Spray Tower can indeed represent a significant investment, one that prompts many to weigh their options carefully. However, long-term savings on maintenance and compliance fines usually tip the scale in favor of installation.
What becomes essential is a clear understanding of the specific needs and the type of tower that would best match those needs. Cost often correlates with the degree of customization and any additional technology integrated into the system. For instance, integrating online monitoring systems might increase upfront costs but reduce long-term operational risks and inefficiencies.
In essence, while budget constraints can limit choices, strategic planning and an eye on future operational efficiency often justify the investment in these robust systems.
The Future of PPH Spray Towers
Looking forward, the industry appears poised for continued growth, especially as environmental regulations tighten globally. The demand for high-quality, efficient emission control systems will only increase. Companies like Shandong Dahuagroup, accessible at their website, are likely to capitalize on this demand by pioneering new technologies and sustainable practices.
Emerging trends suggest an increased integration of IoT technologies for real-time monitoring and predictive maintenance. This evolution is geared towards minimizing downtime and enhancing operational efficiencies, a critical aspect as industries push for greener and more sustainable processes.
To conclude, while the path of China’s PPH Spray Tower technology has been riddled with challenges and learning curves, its transformative potential remains substantial. It’s a journey that mirrors the broader narrative of industrial innovation, one that continually adapts and evolves in response to the ever-changing world around it.
Соответствующая продукция
Соответствующая продукция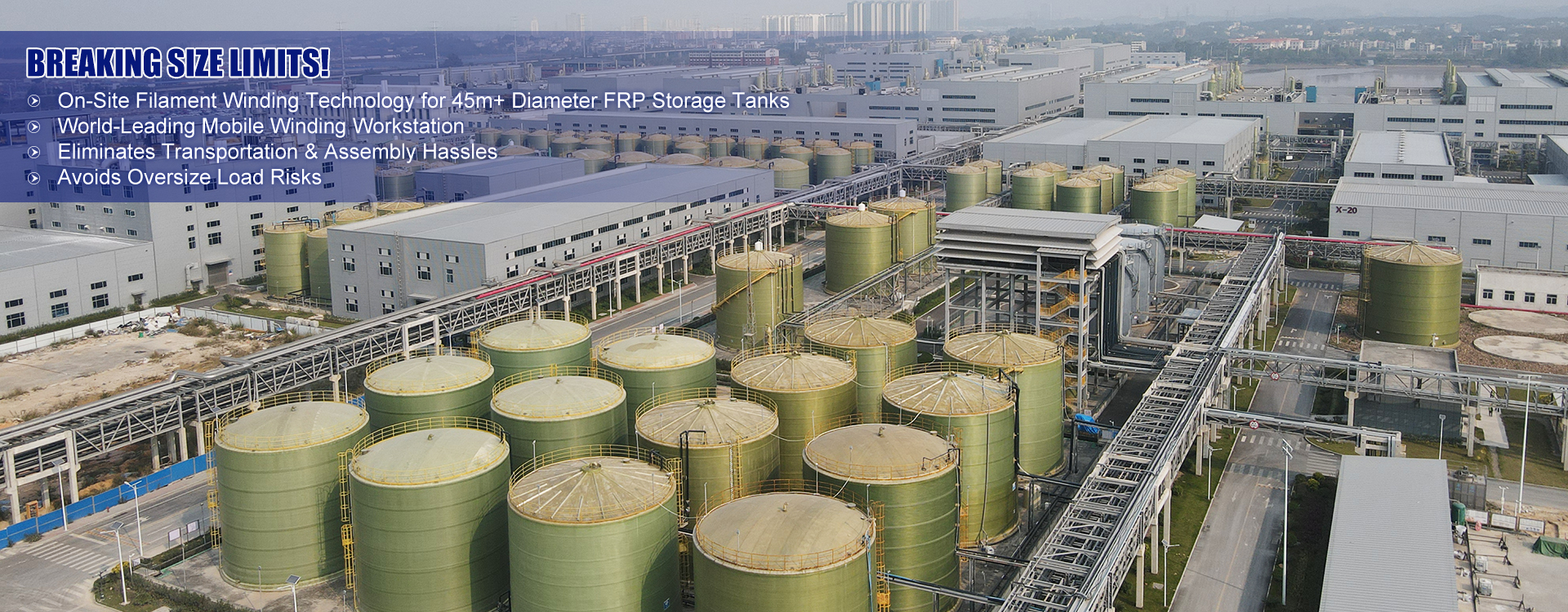
Самые продаваемые продукты
Самые продаваемые продуктыСвязанный поиск
Связанный поиск- OEM Forced-Draft Air Cooler price
- high quality roof mount evaporative cooler factory
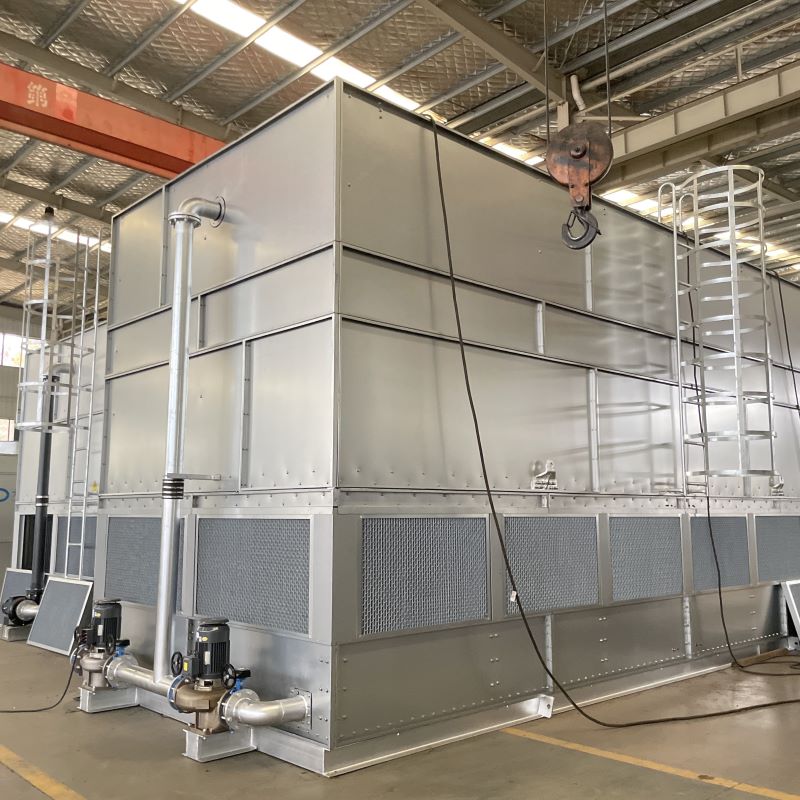
- high quality cooling towers supplier
- China Hydrogen Chloride Exhaust Gas Treatment product
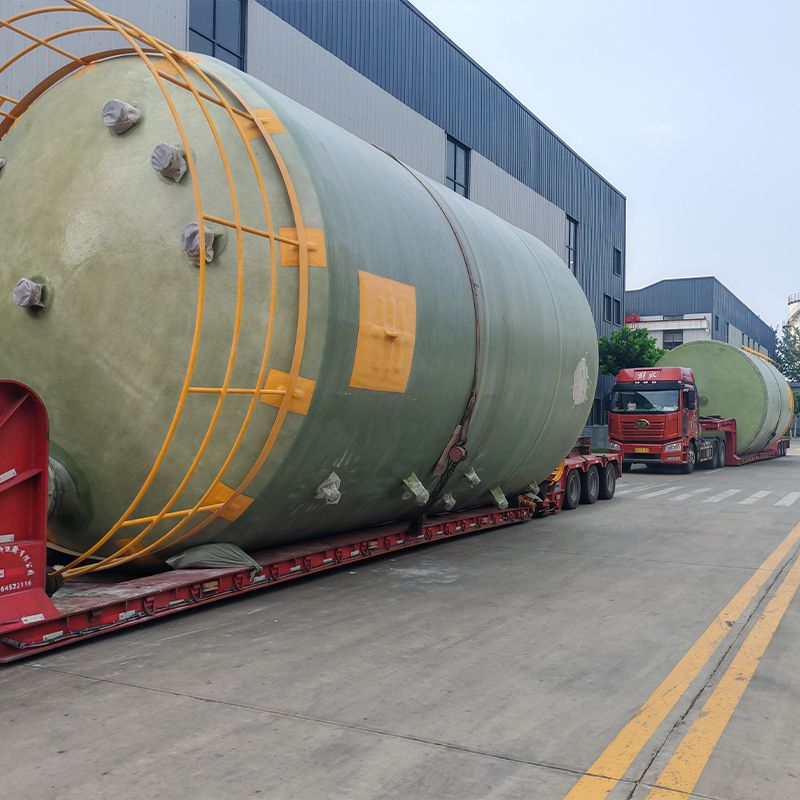
- OEM FRP Storage Tank Supplier factory
- Vertical FRP Storage Tank Equipment
- Best Wet ESP Collection Tube supplier
- China Mist Eliminator FRP Collection Tube supplier
- pentair frp tank product
- Best evaporative cooler with ducting product


























