China Potassium Sulfate Furnace Components
The Complex World of China’s Potassium Sulfate Furnace Components
Understanding the intricacies of China Potassium Sulfate Furnace Components requires not just theoretical insight but also hands-on experience. These components are the silent powerhouse in the agriculture and industrial sectors, with many nuances that even seasoned professionals sometimes overlook. Here’s a closer look at what really goes into these systems.
Foundations of Potassium Sulfate Production
At the heart of potassium sulfate production is the furnace. This isn’t just a piece of metal; it’s a carefully engineered ensemble that must withstand extreme temperatures and corrosive environments. In China, companies like Shandong Dahuagroup, which can be explored further at their website, have been leading the way in refining these components. They’ve faced numerous challenges, notably in material selection. Not every alloy can cope with the unique stresses involved, which means constant innovation is required.
One common issue many firms encounter is maintaining the integrity of these materials under such duress. Several years ago, a colleague in a partner company tried using a supposedly ‘cutting-edge’ material that promised better durability. It failed within months. This underlines a critical lesson: testing in controlled environments can never fully replicate real-world conditions.
The learning curve is steep. Every failure teaches something new about heat distribution, material fatigue, and design optimization. It’s a continuous cycle of assessment and adjustment, always aiming to enhance efficiency and longevity.
Challenges in Component Integration
Integration is another area where these components can become a bottleneck if not handled properly. Matching the various components in the potassium sulfate furnace requires precision and foresight. Even minor misalignments can result in significant operational inefficiencies or, worse, structural failure.
My own experience involved overseeing a large-scale project where we underestimated the subtle differences in tolerances between parts from different suppliers. The alignment was off by mere millimeters, yet it was enough to cause pressure imbalances that took weeks to correct. It’s these kinds of unforeseen details that often trip up ambitious timelines and budgets.
Suppliers like Shandong Dahuagroup understand these pain points well and offer consultation services alongside their product lines to mitigate such risks. Cooperation across departments and partners remains crucial.
Material Advancements and Experimentations
The industry is always on the brink of new material advancements. Every year brings a slew of research articles and patents claiming revolutionary breakthroughs in furnace component materials. However, translating these laboratory successes into manufacturing reality is fraught with challenges.
A past experimental initiative I observed involved utilizing a novel hybrid ceramic-metal alloy designed to handle even greater thermochemical stresses. Theoretically sound, it faced scalability issues. The transition from prototype to mass production revealed unexpected porosity in the materials when formed at large scales, posing severe leakage risks.
Such experiences underscore the value of field trials and scaling studies before any large investment. Yet, without pushing these boundaries, stagnation is inevitable. Experimentation remains the soul of industrial progression.
Maintenance Plans and Longevity
A well-crafted maintenance plan is the unsung hero of any successful potassium sulfate furnace operation. Routine checks and predictive maintenance can mitigate unexpected downtimes. It’s not just about replacing parts when they fail; it’s about anticipating when they might.
There’s a delicate balance between over-maintenance and inadequacy. Too frequent inspections can disrupt operations, while too sparse can invite disaster. In one instance, a three-monthly inspection schedule was shifted to a quarterly approach to minimize downtime. However, this led to an unplanned shutdown due to unnoticed wear in key areas. Lessons learned? Adapt your maintenance strategy to align closely with operational demands and environmental conditions.
Engaging with experts, like those at Shandong Dahuagroup, who can provide detailed analytics and insights on wear patterns, has proven invaluable. Such collaborations can lend an edge in predictive maintenance technology integration.
Future Directions and Considerations
Looking ahead, the focus seems to be on sustainability alongside efficiency. The industry is moving towards more sustainable practices without compromising on the quality or consistency of output. This involves incorporating environmentally-friendly practices and materials while ensuring that the furnace components remain robust.
Emerging regulations regarding emissions and energy consumption are reshaping how companies operate. Adapting to these changes requires staying informed and flexible in operations. Networking within the industry and investing in forward-thinking research holds the key to staying competitive.
In every challenge lies an opportunity. The ongoing evolution of China Potassium Sulfate Furnace Components reflects a broader narrative in industrial processes — one where innovation must constantly meet practical application. Amidst all this, the role of personal experience and industry lore continues to guide us through an ever-complex landscape.
Соответствующая продукция
Соответствующая продукция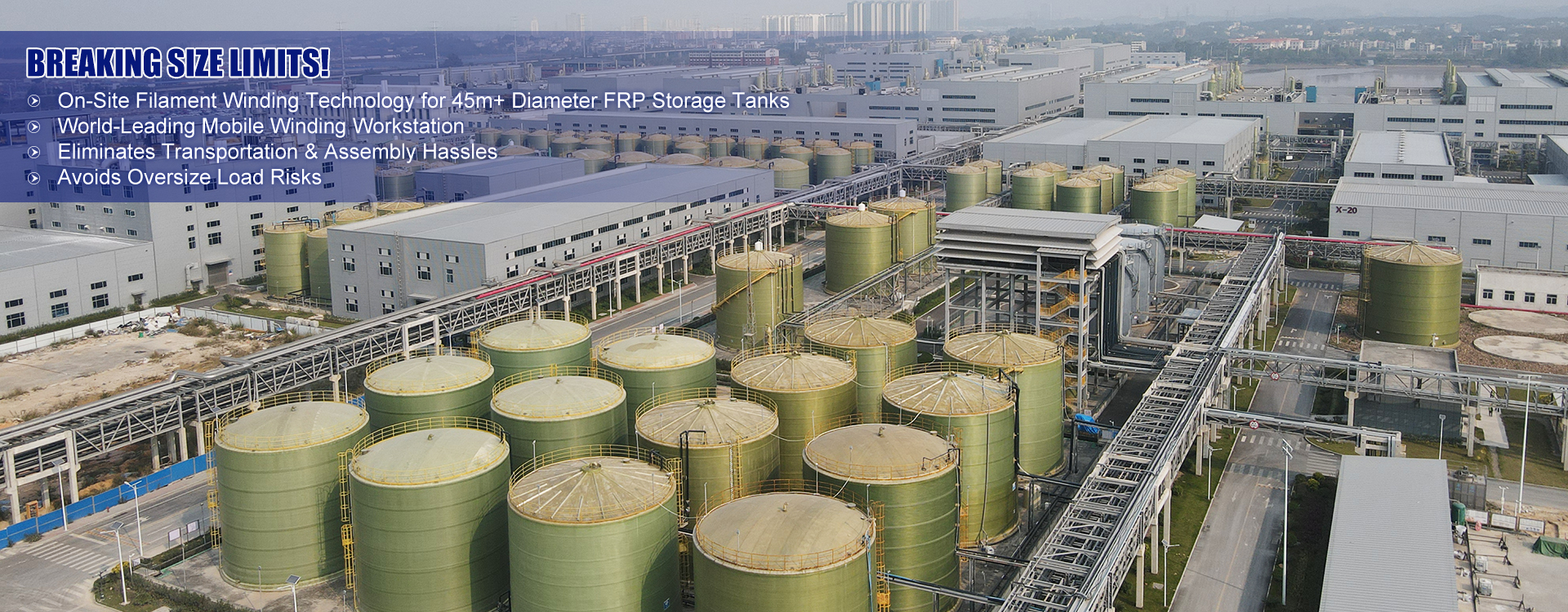
Самые продаваемые продукты
Самые продаваемые продуктыСвязанный поиск
Связанный поиск- PPH Mixing Vessel factory
- Best best evaporative cooler exit
- Best Potassium Sulfate Drag Chain Conveyor Manufacturer
- OEM PPH Mixing Tank factory
- high quality Horizontal FRP Tank Price product
- high quality FRP Storage Tank Supplier
- China rectangular frp tank Manufacturer
- OEM Silicon Carbide Bricks for Mannheim Potassium Sulfate
- Water-Saving Closed-Circuit Cooling Tower product
- high quality FRP Field-Fabricated Large Tank factory


























