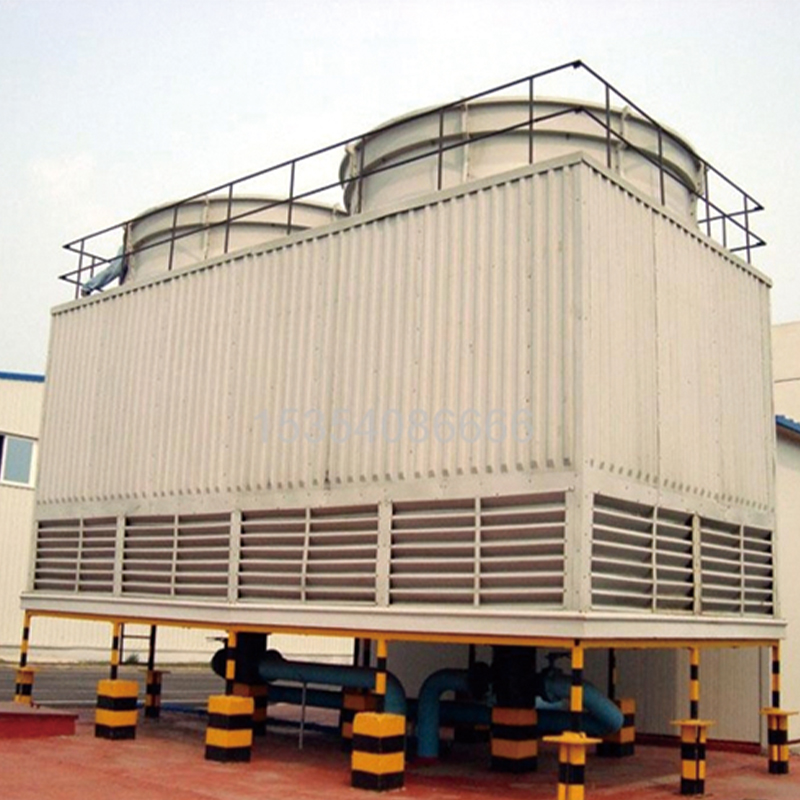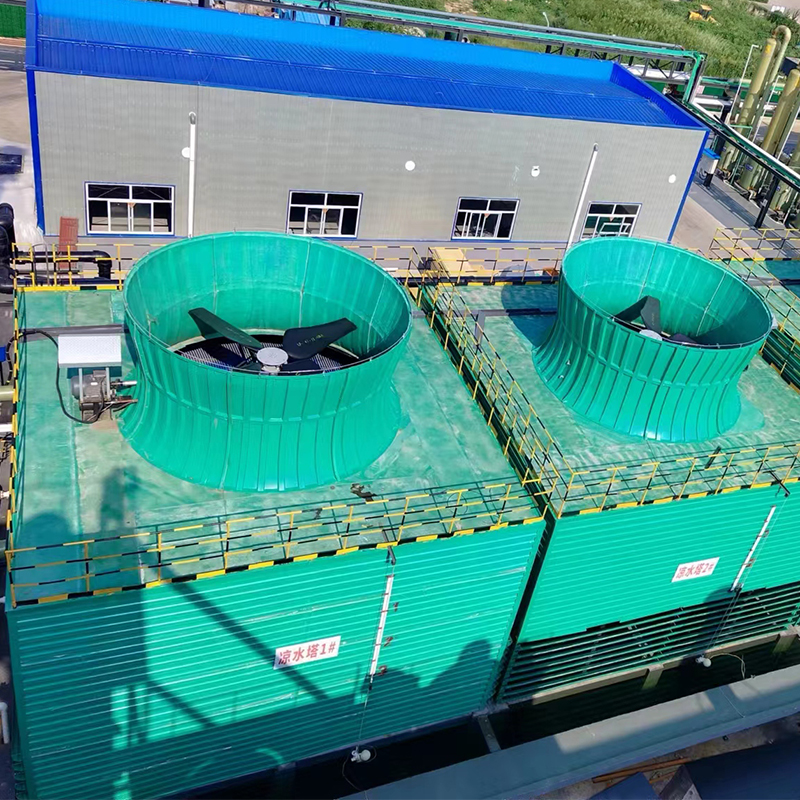
China High-Efficiency Energy-Saving Closed-Circuit Cooling Tower
html
Exploring the Efficiency and Features of China’s High-Efficiency Energy-Saving Closed-Circuit Cooling Towers
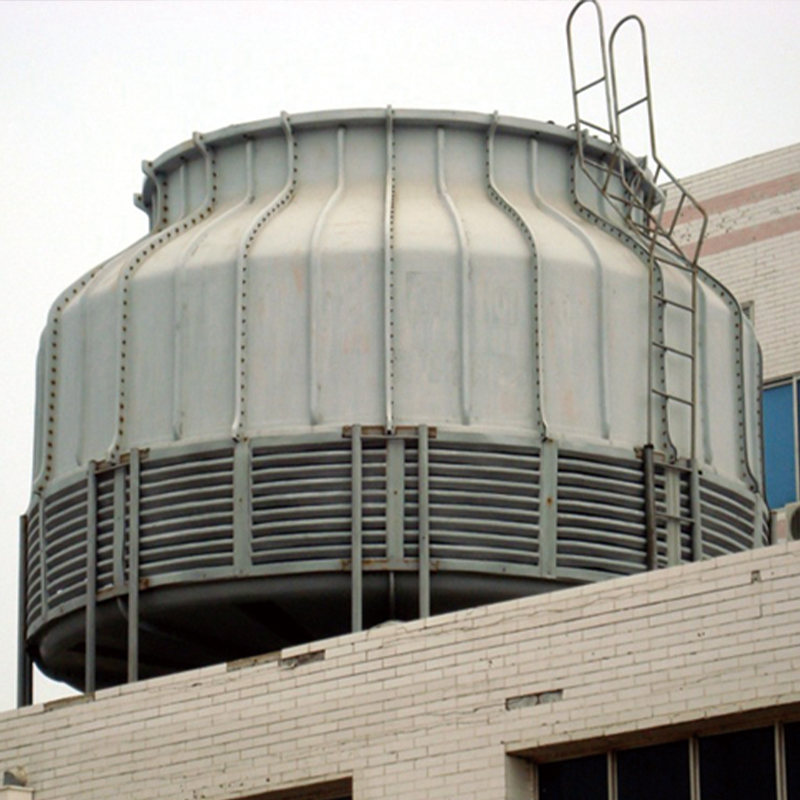
The concept of China High-Efficiency Energy-Saving Closed-Circuit Cooling Tower has been catching the industry’s attention for its potential to reduce energy waste and boost operational efficiency. However, understanding its intricacies requires practical insights, not just theoretical knowledge.
Understanding the Basics of Closed-Circuit Cooling Towers
Often, in the beginning, there's a bit of confusion between open and closed-circuit cooling towers. In this context, closed-circuit towers operate with an isolated loop, preventing contaminants from entering the primary coolant circuit. This seems obvious, but the implications are significant.
One practical observation is how these towers integrate a secondary heat exchanger. More than just a convenience, this piece of equipment plays a critical role. It maintains the quality and efficiency of the cooling fluid, extending the lifespan of the system, which can be particularly beneficial in harsh industrial environments.
Another noteworthy aspect is the maintenance aspect. Unlike open systems, the closed variant tends to require less frequent cleaning, which in itself is an energy and time saver. Noticing this, industries are gradually shifting towards these systems, especially when operating 24/7 isn’t negotiable.
Energy Efficiency in Focus
In my experience, the energy-saving claim isn’t merely a marketing line but rather a tangible benefit. For instance, units designed and manufactured in China have demonstrated a steady reduction in operation costs by optimizing water usage and reducing heat losses.
The key here lies in the heat exchange process. Given my exposure to various installations, the precision and design of the coils can dramatically influence performance. Chinese manufacturers have been advancing these designs meticulously, ensuring each coil offers maximal surface area contact with the cooling medium.
Real-world scenarios have shown up to 30% energy savings when transitioning from standard models to high-efficiency variants. This figure can vary based on numerous factors, but it evidently showcases the potential locked within this technology.
Challenges and Considerations
Despite the benefits, challenges exist. Installing a closed-circuit cooling tower isn't without its hurdles. The initial setup cost, for example, can be daunting. In projects I’ve been involved with, budget constraints often push for compromises elsewhere.
Moreover, placement and environment play a huge role. A cooling tower needs to be situated in an area that allows for optimal airflow and minimal external contamination, ensuring the ultimate efficiency and longevity. Getting this wrong could negate some of the benefits claimed by the manufacturers.
It’s important to note that regular inspections and maintenance are still crucial. Issues like scaling and fouling, while less prevalent, can still occur and diminish the tower's performance if left unchecked.
Setting Up for Success
The success of a cooling tower installation is often contingent upon proper integration with existing systems. At sites such as www.sddahuagroup.com, they emphasize tailored solutions to ensure compatibility and efficiency.
Customizing the setup to suit specific operational requirements is key. This involves consideration of flow rates, temperature differentials, and environmental impacts — factors that experienced technicians tend to navigate intuitively, perhaps perfected through years of troubleshooting similar systems.
Collaboration between engineers and the supplier is critical. It ensures that all technical requirements align with the practical realities of the industry — something a cookie-cutter solution might overlook but can be a hurdle crossed with proper planning and expertise.
A Look To The Future
What the future holds for China High-Efficiency Energy-Saving Closed-Circuit Cooling Towers is promising. With ongoing advancements in materials and technology, efficiency continues to improve, and operational pitfalls are being systematically addressed.
Global demand for energy-efficient solutions keeps rising, and with China’s extensive manufacturing capabilities, the gap between innovation and accessibility is closing faster than ever. The eco-friendly appeal is also gaining traction internationally, projecting a growth trajectory that seems sustainable.
Ultimately, those of us embedded in the industry recognize the potential these systems hold. While not a one-size-fits-all solution, with careful implementation, they present a formidable step towards reducing the carbon footprint of industrial operations globally.
Соответствующая продукция
Соответствующая продукция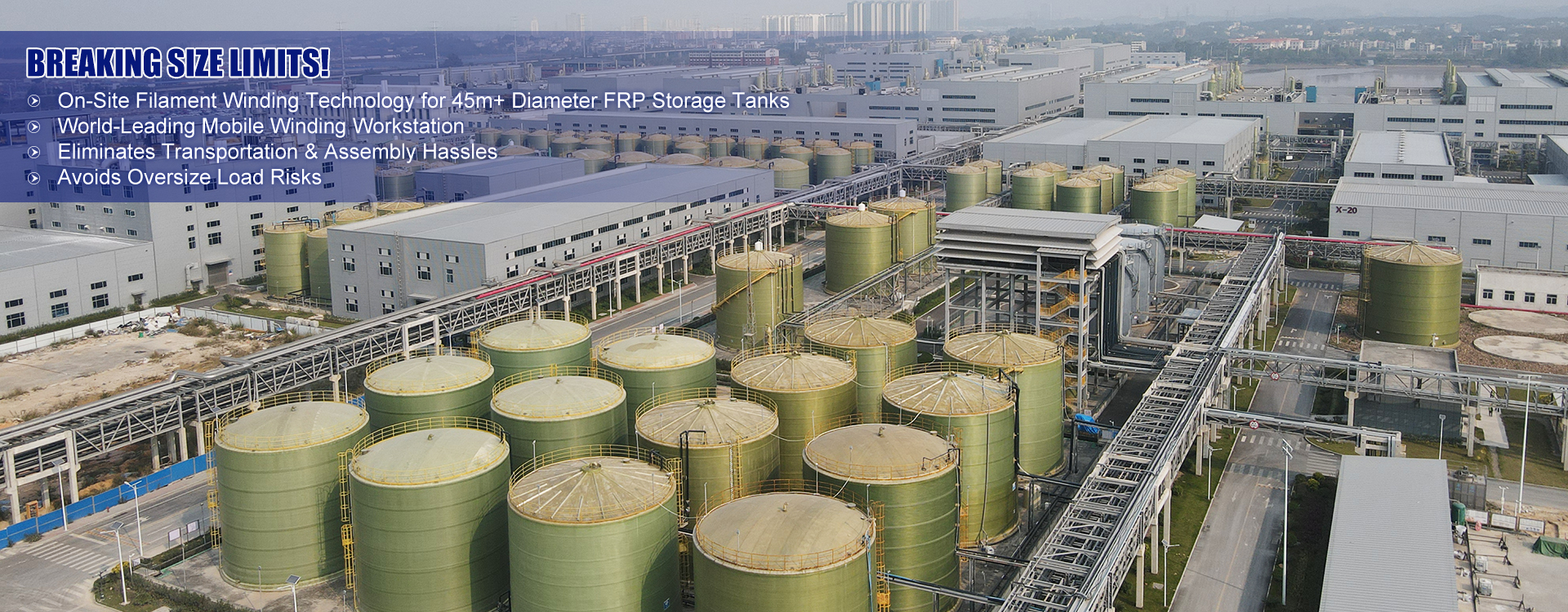
Самые продаваемые продукты
Самые продаваемые продуктыСвязанный поиск
Связанный поиск- Best FRP Collection Tube Pricing product
- high quality Potassium Sulfate EPC Project price
- evaporative cooler for garage exit
- Best round evaporative cooler factory
- China gfrp tank price
- Best FRP Chimney price
- OEM Potassium Chloride Drag Chain Conveyor exit
- Best Vertical FRP Hydrochloric Acid Tank factory
- OEM cooling towers exit
- Best FRP Hydrochloric Acid Tank Manufacturer
























