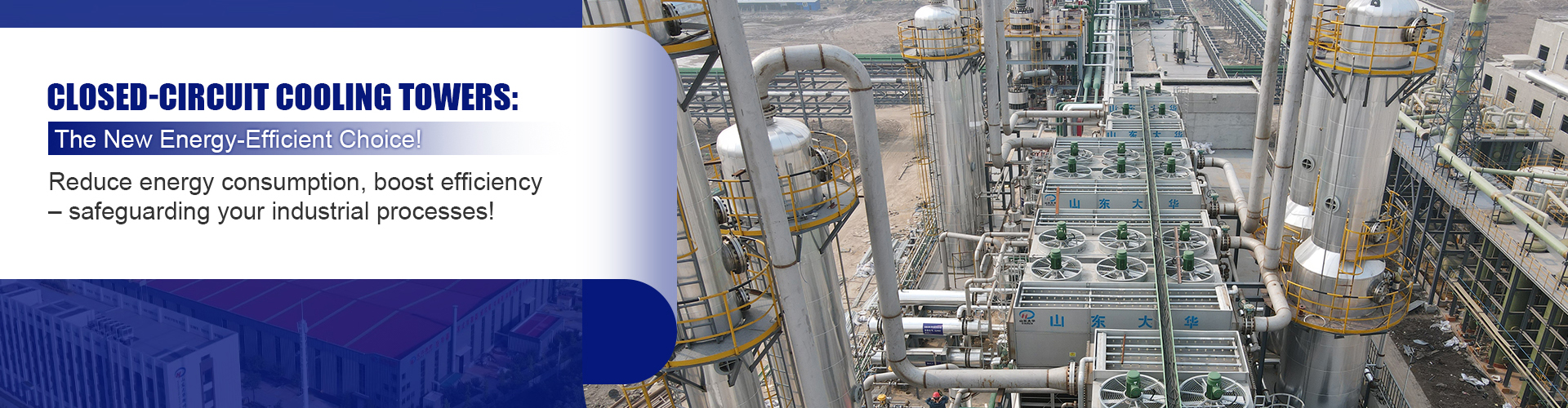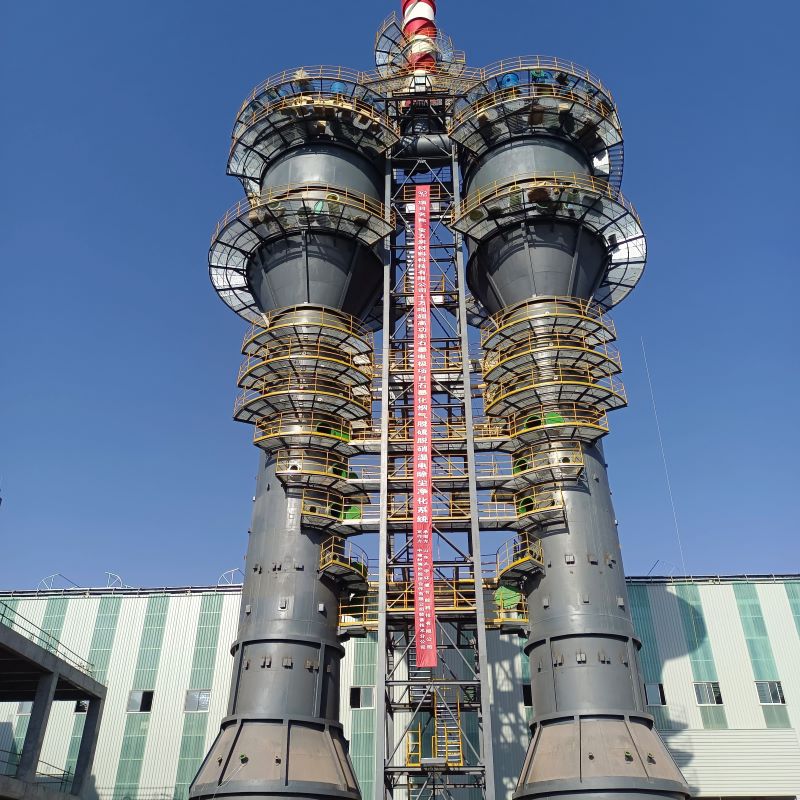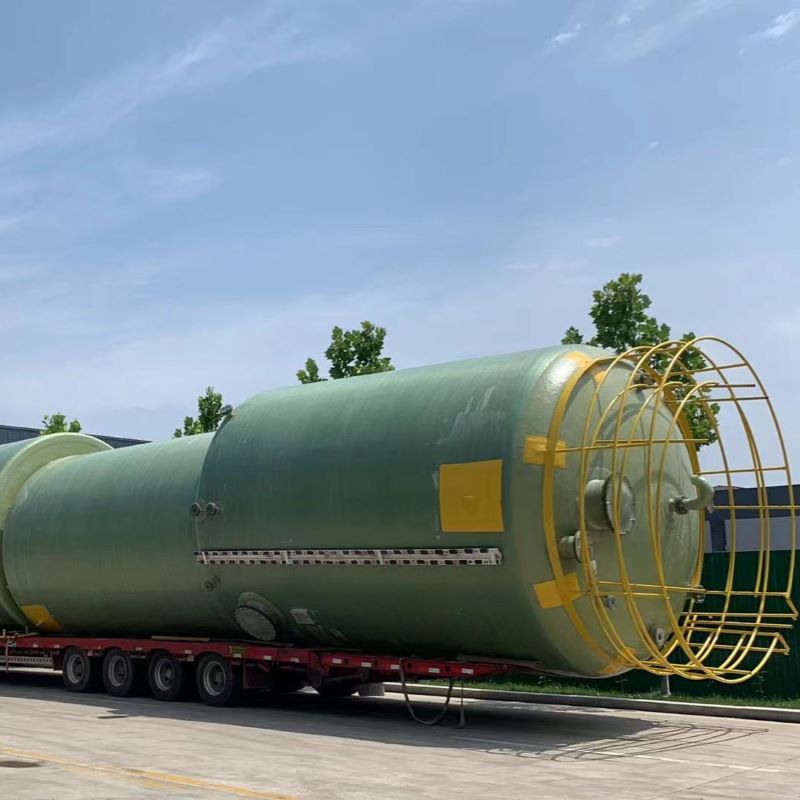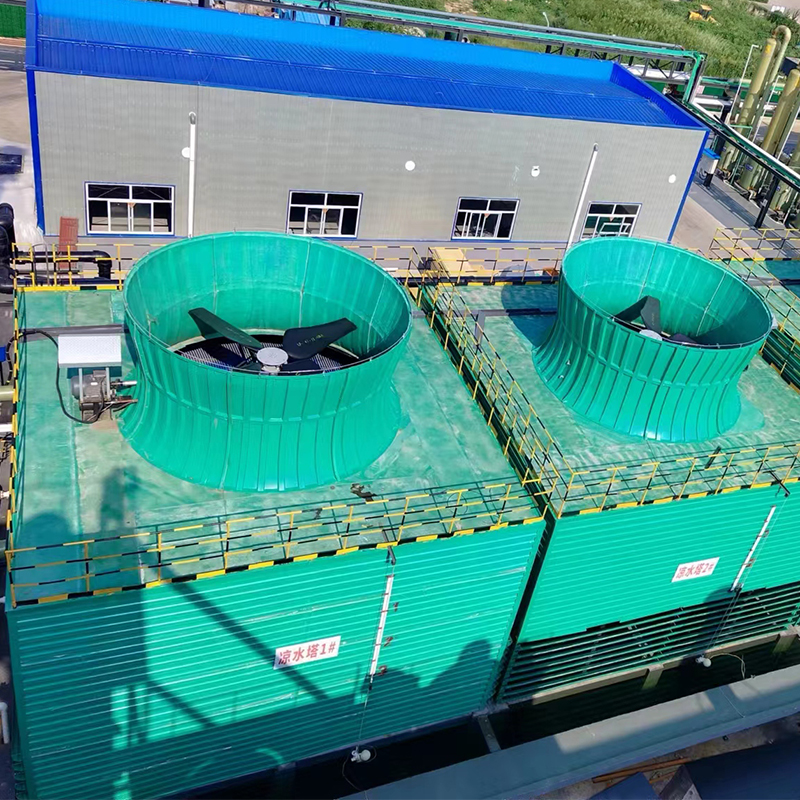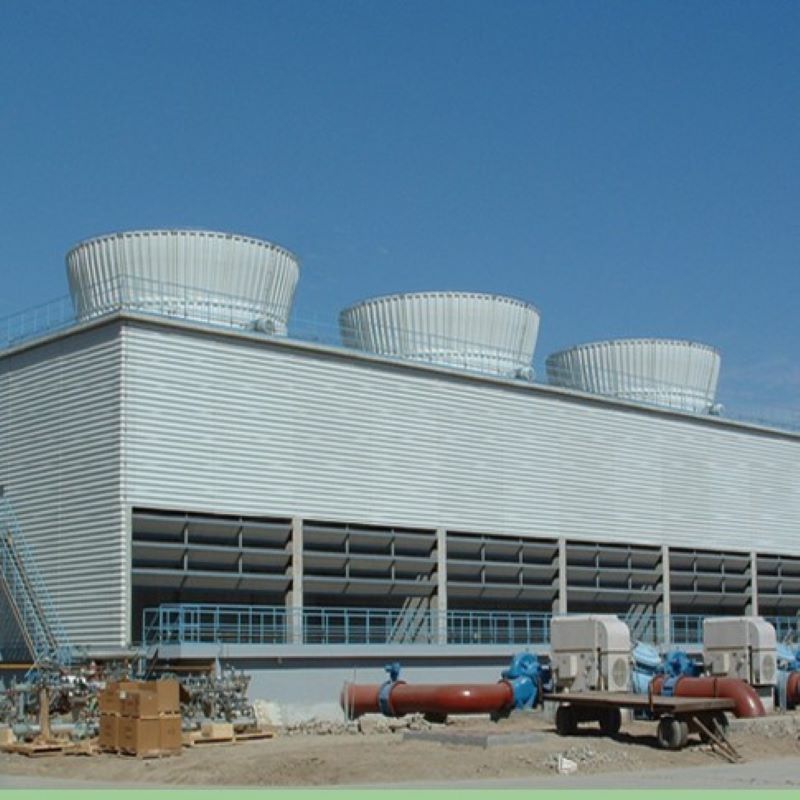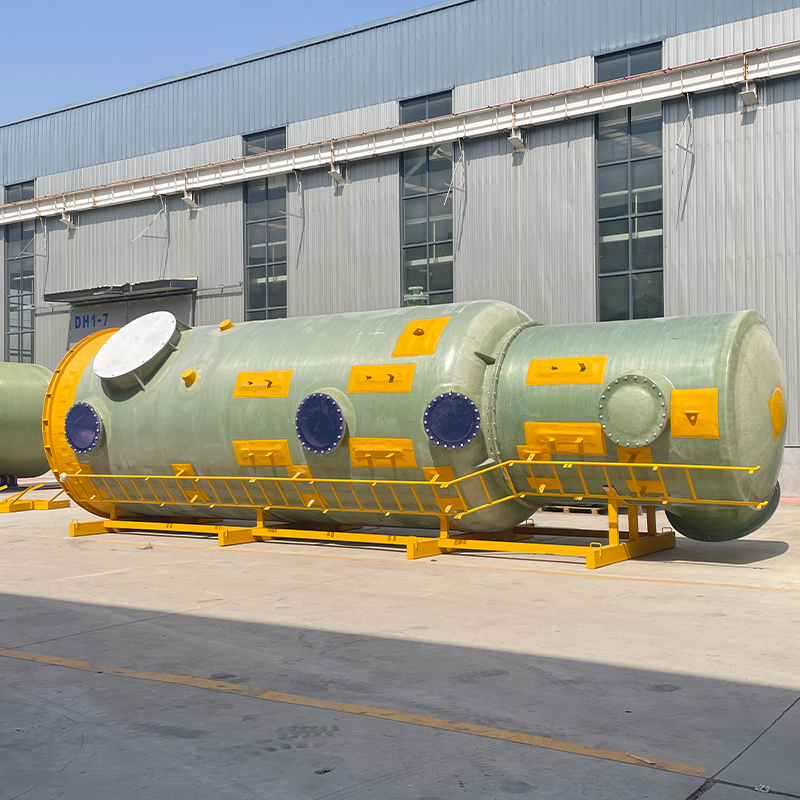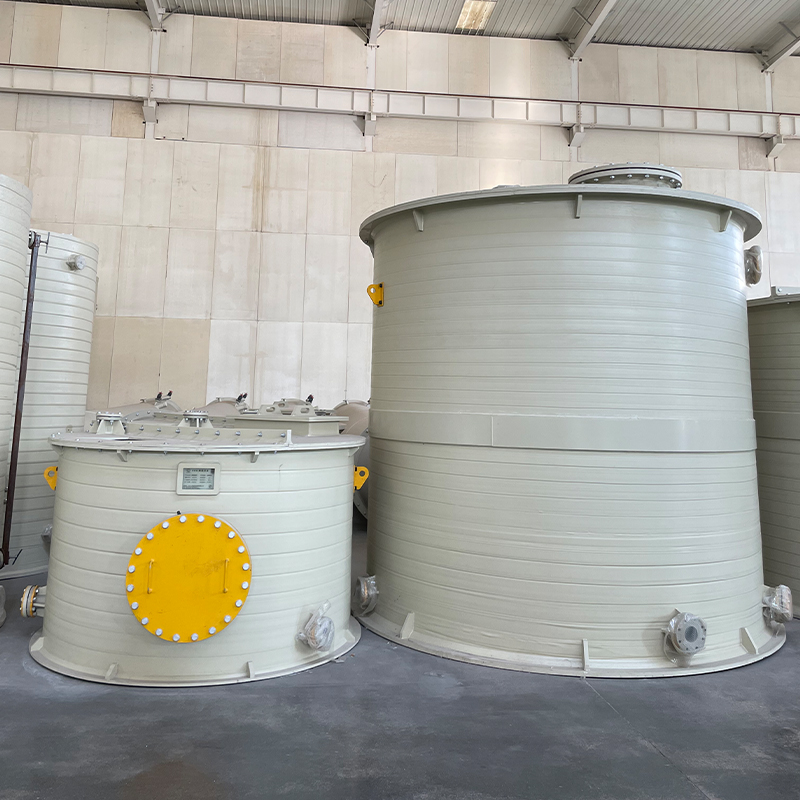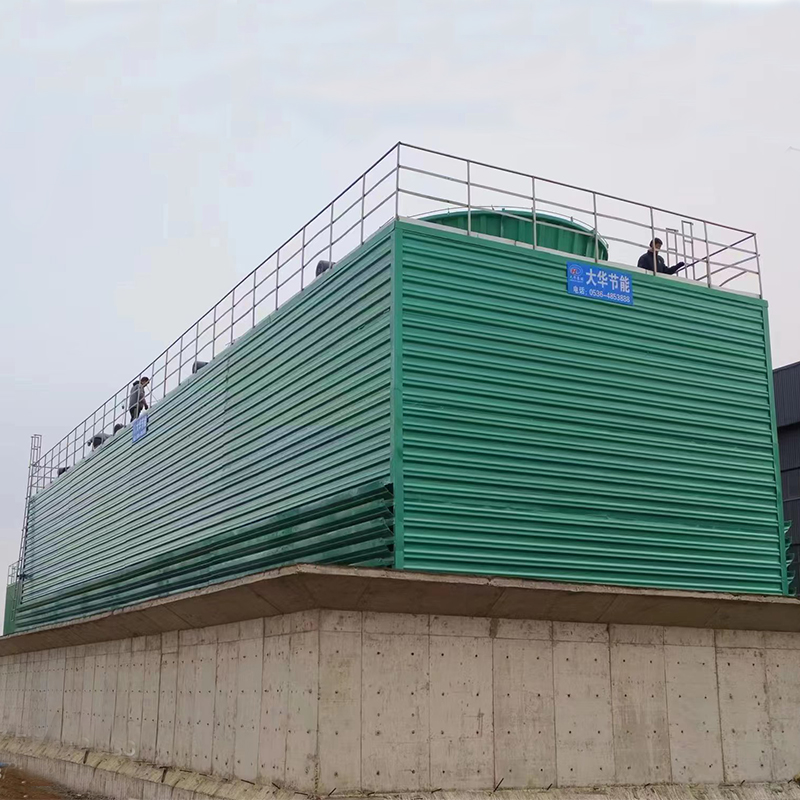
China Filament-Wound FRP Process Piping
Understanding the Complexities of China Filament-Wound FRP Process Piping
The world of China Filament-Wound FRP Process Piping is as intricate as it is essential. When diving into this subject, it's easy to get lost in the technical specifications and industry jargon. Yet, at its core, it is about craftsmanship, material science, and the delicate balance of engineering precision. This piping solution is revolutionizing many sectors in China, yet misconceptions persist, especially about its environmental durability and cost-effectiveness.
The Significance of Filament-Wound FRP Piping
In discussions about infrastructure advancements, filament-wound Fiber-Reinforced Plastics (FRP) often play a pivotal role. With China leading the charge in industrial applications, the importance of this technology is magnified. But what makes it so special? It's not just a matter of replacing traditional materials like steel or concrete; it's about introducing a material that offers a unique combination of light weight and high strength.
I remember, during a project a couple of years back, the goal was to replace existing metal pipelines in a chemical plant with something more durable against corrosive substances. The filament-wound FRP pipes proved advantageous due to their resistance to chemical attacks and ease of installation. But that's not where the story ends, as I'll delve further into some implementation stories that highlight their versatility.
One challenge, however, is that while the material itself is resilient, the precision in the winding process is what determines its eventual performance. A minor deviation during the filament winding could compromise the structural integrity, which often gets overlooked by those new to the technology.
Challenges in Adoption
Despite its benefits, adopting such advanced materials isn't without hurdles. In the past, some companies hesitated to switch to FRP due to upfront costs. An oversight, often, since longer-term savings on maintenance and replacement costs outweigh initial investments. But changing mindsets takes time. I recall a specific meeting with a mining company where convincing the board involved laying out the detailed lifecycle cost comparisons.
Another complexity lies in the installation techniques. Unlike traditional systems, FRP requires trained professionals to handle the filament-winding machinery adeptly. A lesson learned the hard way when an installation crew miscalculated the tension required, resulting in a structural fault. Retraining became a crucial part of the transition process after that mishap.
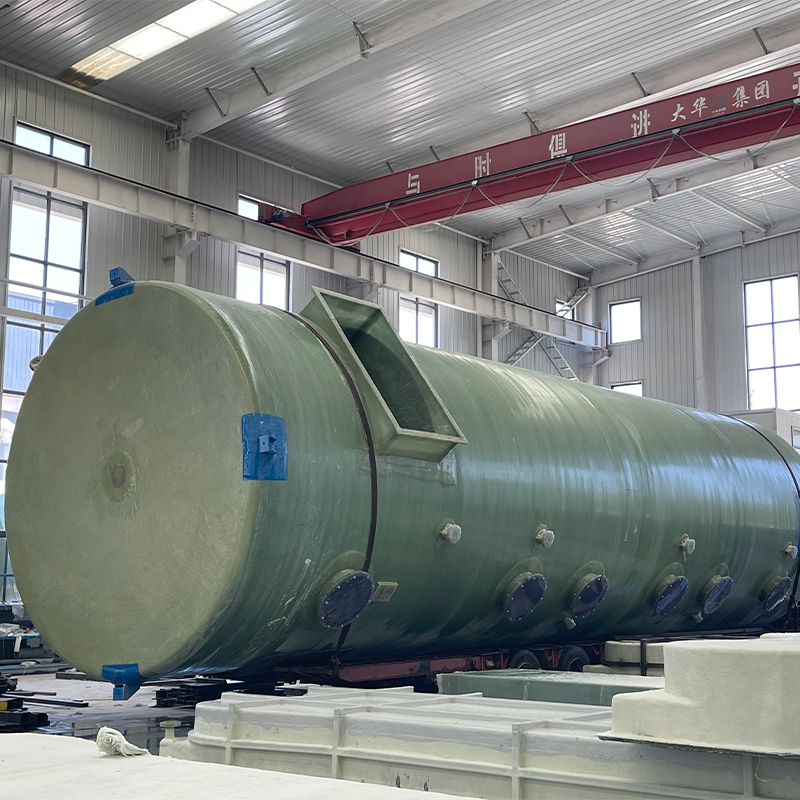
Moreover, while working with companies like those covered at Shandong Dahua Group, it's evident that successful adoption often involves close partnership with suppliers familiar with regional regulations and standards.
Quality Control in the Fabrication Process
During my time overseeing a fabrication unit, maintaining stringent quality control was at the forefront. The filament-winding process itself involves a sophisticated dance of multiple parameters—everything from resin mix to fiber alignment impacts the final product. Ensuring consistency requires a regime of regular inspections and calibrations.
At Shandong Dahua Group, we found value in introducing automation to monitor each phase of production, minimizing human error. Interestingly, even automation isn't foolproof. It's about striking the right balance between human oversight and machine precision.
Furthermore, aligning the products to withstand local environmental stresses meant customizing resin formulas to combat issues such as UV exposure or thermal variations, something rarely accounted for during initial planning but crucial for longevity.
Application Success Stories
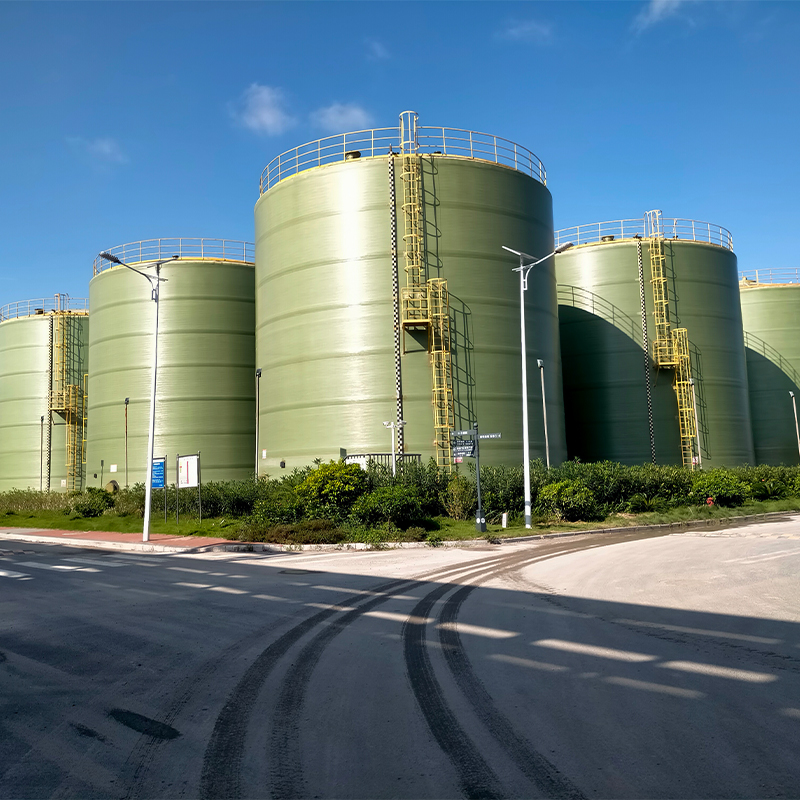
There are numerous instances where China Filament-Wound FRP Process Piping has marked a milestone in practical applications. A standout case involved a desalination plant where traditional materials failed prematurely due to constant exposure to saline environments. Switching to FRP piping extended the operational lifetime by nearly 40%.
At another site, involving a municipal water project, the lightweight nature of FRP enabled faster and less costly transportation to remote areas, where traditional materials would have been logistically cumbersome.
These cases are emblematic of FRP's potential. But they also remind us of the ongoing need for comprehensive planning and meticulous execution to harness the material's full capabilities.
Future Prospects and Technological Innovations
What’s ahead for China Filament-Wound FRP Process Piping? With continued research, the industry is on the brink of introducing even more advanced resins and fibers that promise better performance metrics. Increased collaboration between Chinese manufacturers and global tech firms is another trend driving innovation.
Efficiency and sustainability are currently hot topics, with many looking at how the lifecycle of FRP can be optimized further. Green manufacturing practices and the integration of recyclable components into the FRP matrix are among the exciting avenues being explored.
Ultimately, the growth trajectory for this industry hinges on education and awareness—dispelling myths and promoting the tangible benefits FRP can offer. As industry practitioners, our role involves not only adapting but also leading these conversations towards more sustainable and efficient infrastructure solutions.
Соответствующая продукция
Соответствующая продукция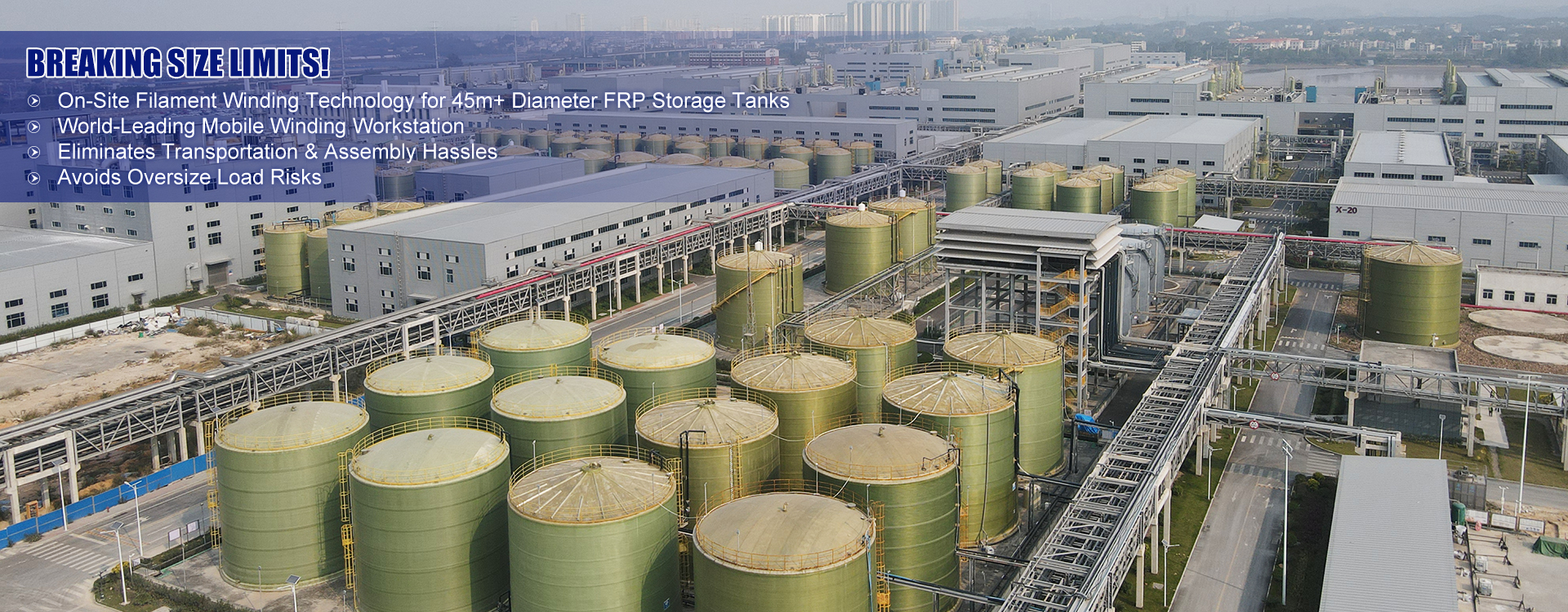
Самые продаваемые продукты
Самые продаваемые продуктыСвязанный поиск
Связанный поиск- OEM Evaporative Air Cooler
- Best FRP Mixing Tank Manufacturer price
- OEM Horizontal FRP Storage Vessel Manufacturer exit
- rectangular frp tank product
- China FRP Mixing Tank product
- high quality Evaporative Air Cooler
- China Shandong Potassium Sulfate Furnace Parts product
- Horizontal FRP Tank Manufacturer price
- Wet Electrostatic Precipitator Manufacturer factory
- high quality starlite frp tank factory























