China Condenser
Understanding China Condenser: Insights from the Field
When discussing the role of a China condenser in industry settings, it's essential to wade through some misconceptions. Many believe these components are simple and universal. However, my years in the field have taught me otherwise—each condenser has its own story and specifics.
The Critical Role of Condensers
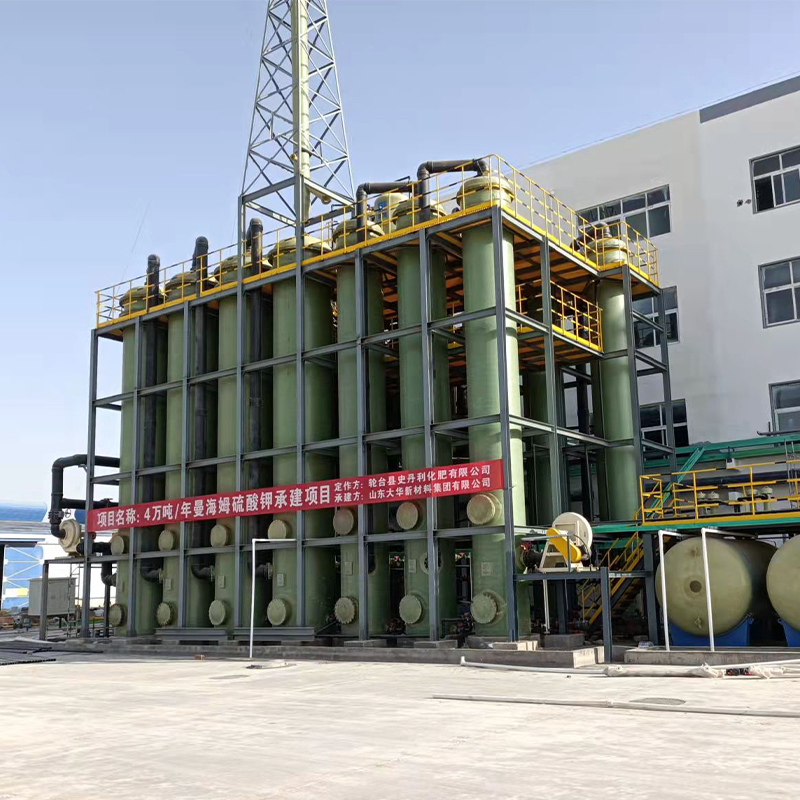
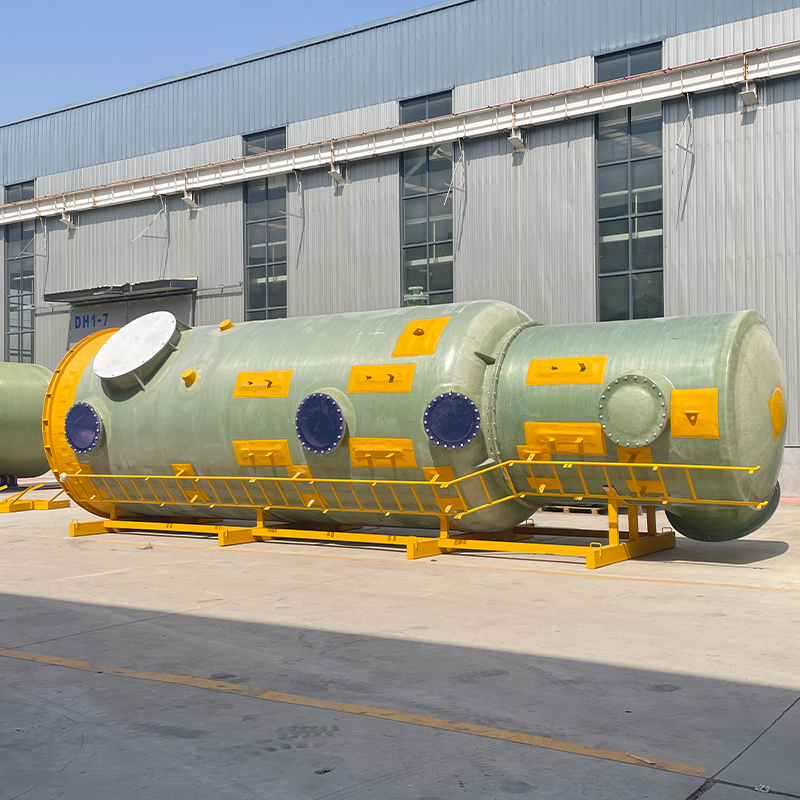
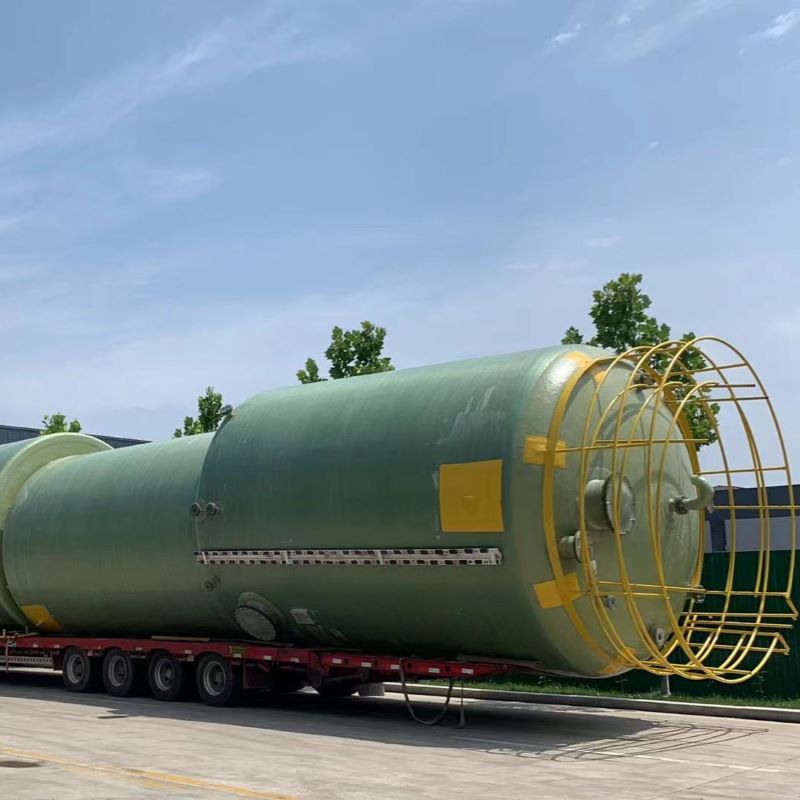
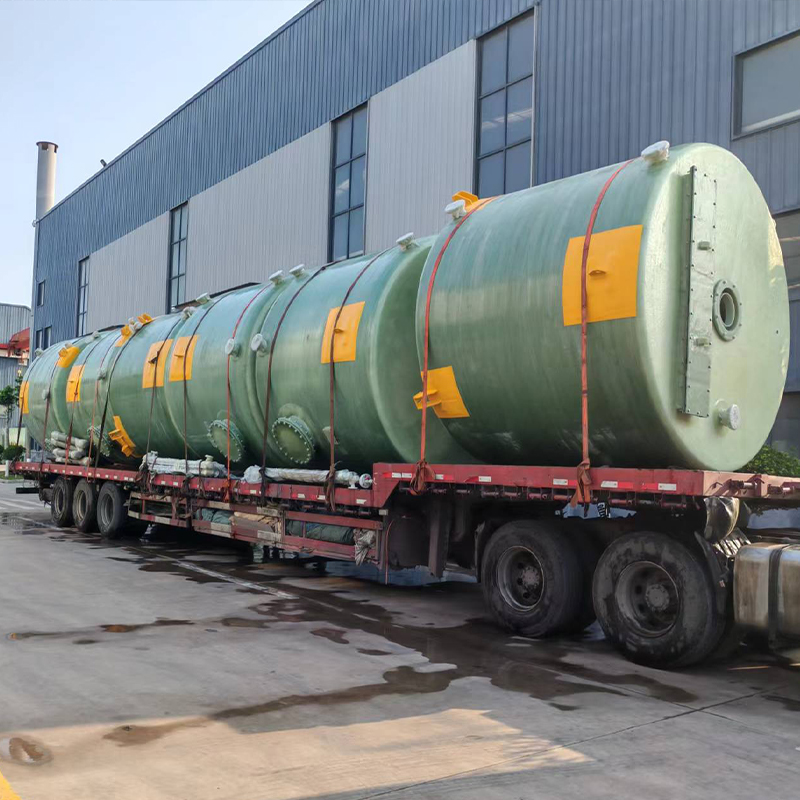
Condensers are often overlooked yet crucial in industrial applications. In practical terms, they transform vapor into liquid, focusing on thermal exchange. In China, the market is particularly vibrant, with manufacturers continually pushing the technological envelope.
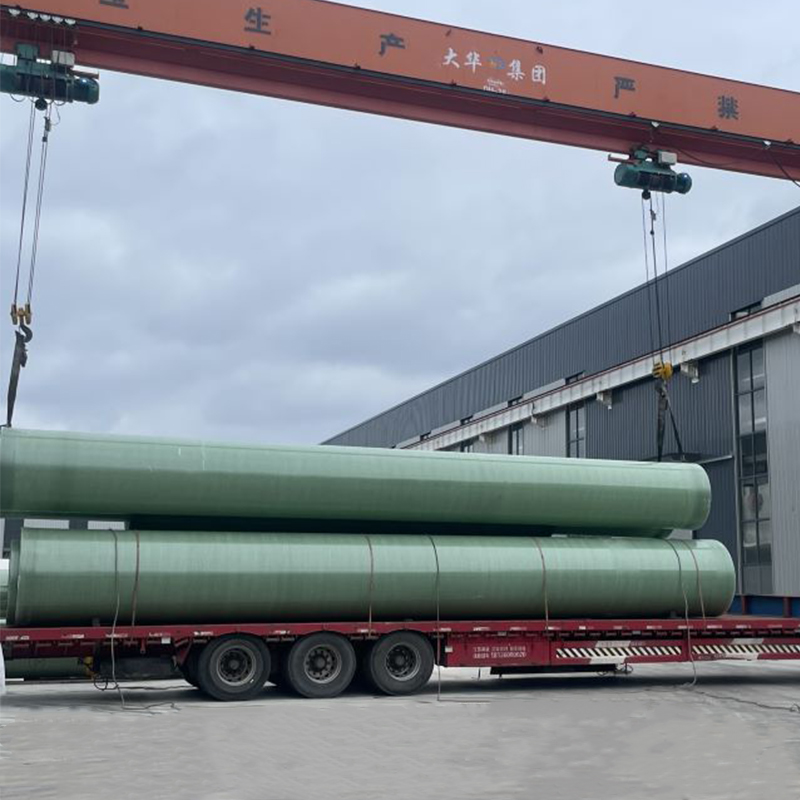
During a recent visit to a factory in Shandong, I witnessed the assembly of a new model. The precision and innovation on display were remarkable. Engineers were tweaking designs based on feedback loops from various industries, confirming that user-driven innovation is alive and kicking here.
Yet, challenges remain. The China condenser must withstand diverse environmental conditions, from coastal humidity to inland dust storms. Many domestic companies are now incorporating advanced materials to enhance durability, something that was seldom prioritized a decade ago.
Technological Advances and Challenges
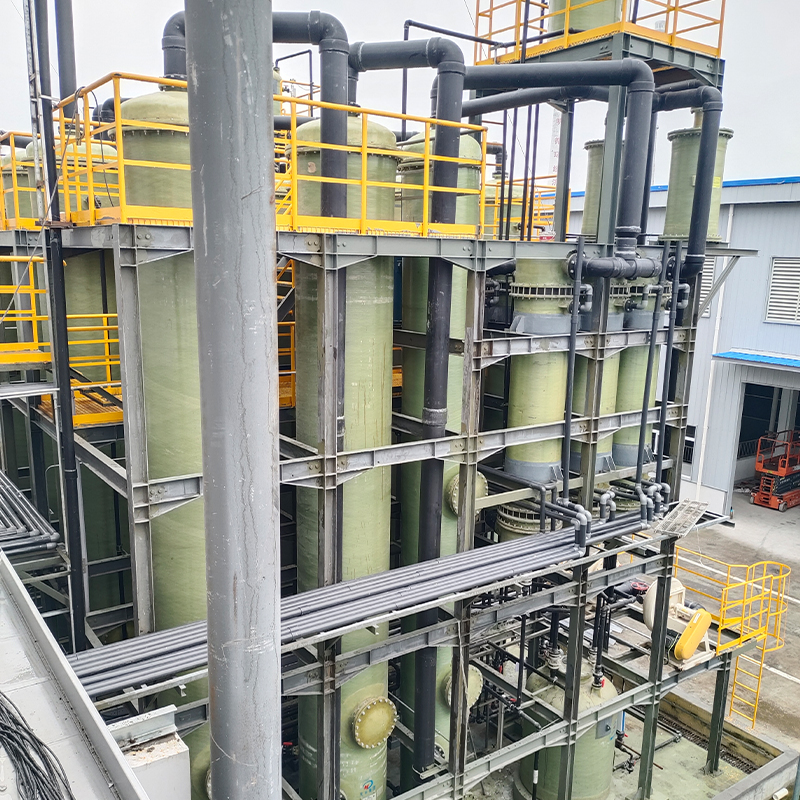
Technology has advanced, but so have expectations. High-efficiency demands lead manufacturers to explore new methods, but sometimes initial prototypes fall short. I've seen it happen—ambitiously designed models unable to sustain the necessary thermal dynamics under rigorous testing.
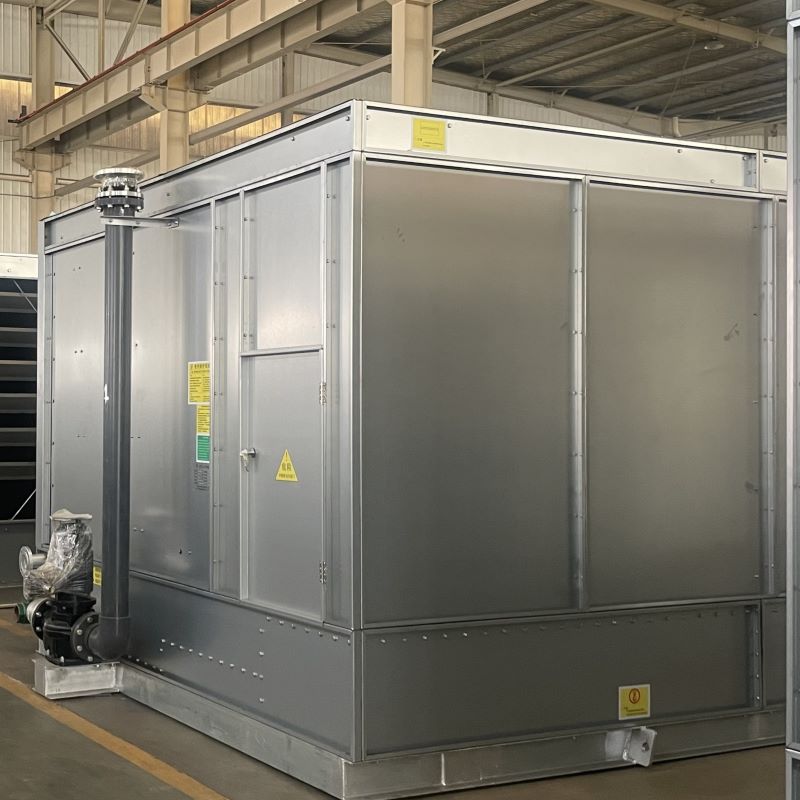
The choice of materials also greatly impacts a condenser's performance. Stainless steel was the standard for years, yet now there's a shift towards composites and alloys, offering better thermal efficiency and cost-effectiveness.
Companies like those found at SD Dahua Group are spearheading these explorations. They focus on product longevity, ensuring solutions meet stringent industrial needs—a testament to the country's growing engineering prowess.
Hands-On Experience: Case Studies
Real-world applications often paint a different picture than theoretical models. In a textile mill I consulted, a new condenser design promised energy savings. However, it introduced unforeseen maintenance complexities. Such instances underscore the necessity for ongoing support and adaptation.
The situation improved once adjustments tailored to the specific factory conditions were made. The lesson was clear: flexibility in design and deployment is as crucial as initial specifications.
This case also showed the importance of collaboration between engineers and end-users—a facet often under-discussed. Both parties need to communicate openly for optimal outcomes.
Future Trajectories in the Condenser Market
Looking forward, the China condenser market is expected to innovate further. As environmental regulations tighten, emphasis on eco-friendly technologies will likely increase. This shift will drive research into alternative refrigerants and more efficient thermal exchange processes.
Increasing digitalization means more data from operational condensates—leading to smart monitoring systems. Predictive maintenance can minimize downtime, a feature gaining traction among large-scale industrial clients.
One cannot overlook the importance of global cooperation. Despite current geopolitical tensions, technology exchange remains active, offering opportunities to learn from each other's advancements.
Final Thoughts: Navigating the Market
For those involved in or entering the industry, understanding the nuances of a China condenser can spell the difference between success and failure. Don't underestimate the importance of real-world testing and iterative design processes.
And as I’ve learned, keep your eyes on emerging technologies and regulatory changes. Those who adapt not just survive but thrive in this competitive landscape.
With the right approach and informed decisions, companies stand to gain significantly, not just in economic terms but also in fostering sustainable industrial growth.
Соответствующая продукция
Соответствующая продукция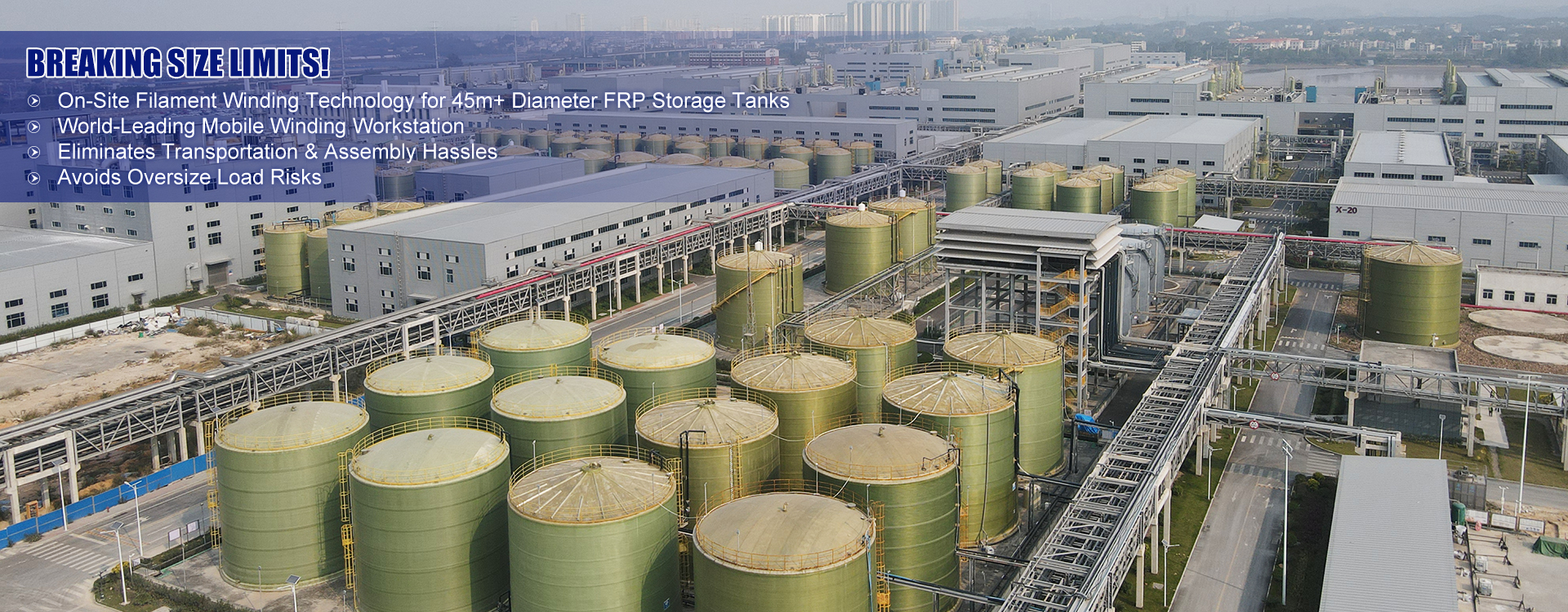
Самые продаваемые продукты
Самые продаваемые продуктыСвязанный поиск
Связанный поиск- FRP agitation tanks price
- China frp tank and vessel
- high quality Horizontal FRP Storage Vessel factory
- China evaporative coolers for sale Manufacturer
- high quality High-Alumina Bricks for Mannheim Potassium Sulfate exit
- Evaporative Cooler Manufacturer
- OEM 2 stage evaporative cooler exit
- China Horizontal FRP Storage Vessel Manufacturer factory
- Best FRP Process Tank Manufacturer
- High-Efficiency Refrigeration Closed-Circuit Tower factory
























