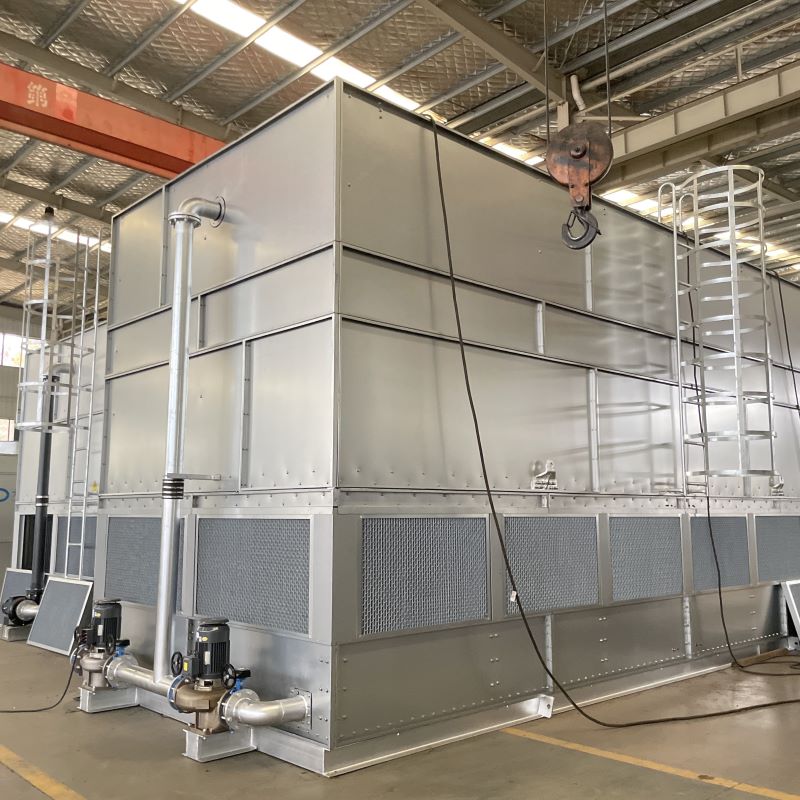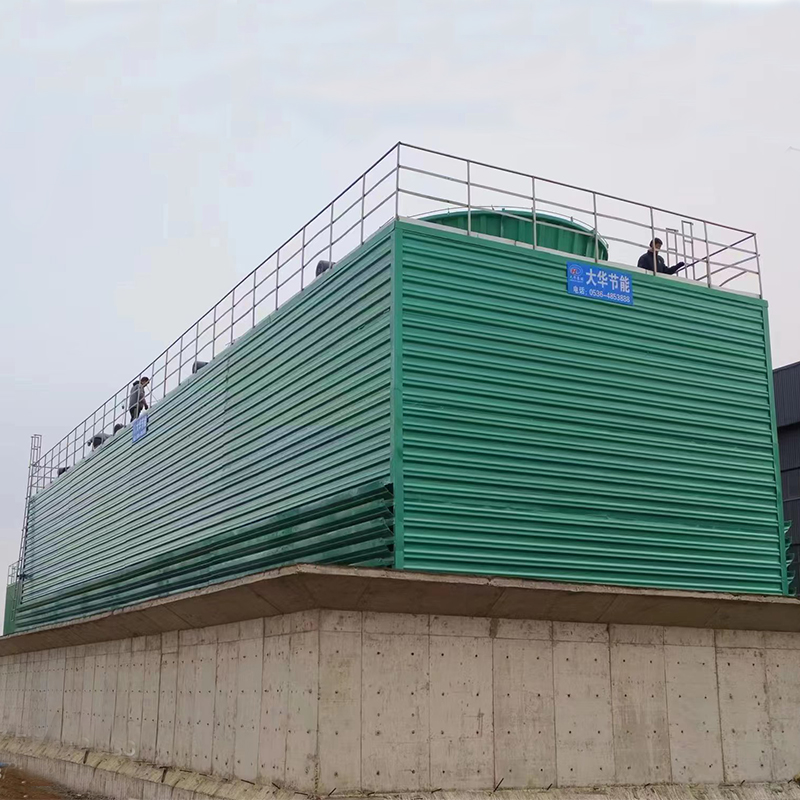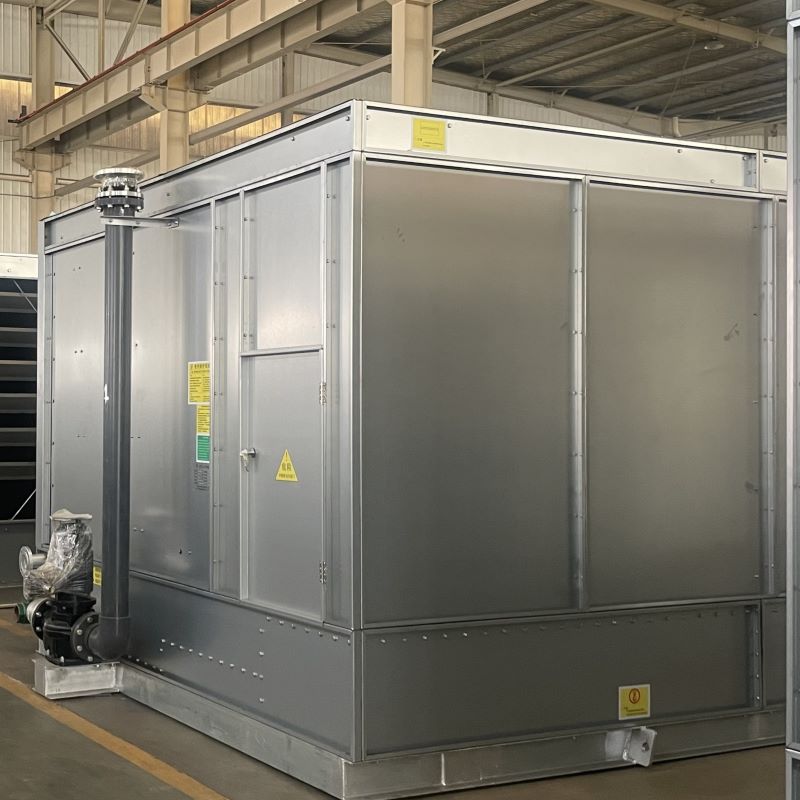
10000 cfm evaporative cooler
Understanding the 10000 CFM Evaporative Cooler
What makes the 10000 CFM evaporative cooler tick? For industry insiders, it's not just about size or capacity; it's about understanding the interplay of factors like ambient humidity, airflow, and installation precision. These elements can turn theoretical performance into practical reality—or disappointment.
The Basics of CFM and Why It Matters
When discussing evaporative coolers, one term that often pops up is CFM, or Cubic Feet per Minute. It's a measure of the air volume an evaporative cooler can process. So, a 10000 CFM evaporative cooler isn't just randomly numbered—it's designed to handle a specific air volume ideal for large spaces.
Getting the right CFM is crucial. Too little, and your cooling efforts are in vain; too much, and you may find yourself overpaying for unnecessary power. Think of it as finding the sweet spot in Goldilocks' zone. Real-world conditions aren't as straightforward, though. For instance, I've seen warehouses where a 10000 CFM unit worked perfectly due to optimal placement and low humidity levels.
It's not uncommon to oversize a cooler initially. Many businesses I've interacted with prefer ensuring excess capacity rather than risking undersizing, especially in unpredictable climates. However, properly assessing needs with a detailed site survey often optimizes both performance and cost.
Challenges and Missteps in Installation
Even the best equipment falters if mishandled. One frequent mistake I've witnessed is poor placement. The effectiveness of a 10000 CFM unit can drastically decrease if airflow is obstructed. Experienced technicians know to account for obstacles and leverage the building's natural airflow patterns.
Peripheral issues also arise during installation. Take water supply, for instance. Efficient flow is critical, and yet it's often an afterthought. I recall a case where a large facility faced cooling failures, only to discover the culprit was inadequate water pressure.
Maintenance is another hurdle. Unlike simpler devices, evaporative coolers need regular upkeep. Pads, pumps, and fans—each part demands attention. Effective, scheduled maintenance means minor repairs, but ignoring it invites serious system failures.
The Impact of Humidity
Humidity plays a pivotal role. In areas with high moisture, the performance of an evaporative cooler can dip significantly. Imagine trying to wring out a saturated sponge—it’s a similar struggle for these units trying to cool damp air.
I've seen situations where businesses underestimated humidity's effect. The initial cooling was promising, but efficiency waned as the season's dampness calcified. It's vital to understand this dynamic, rather than attribute diminished performance solely to equipment faults.
Mitigating such issues often involves pairing systems with dehumidifiers or adjusting operational times, emphasizing adaptability over a one-size-fits-all mindset.
Choosing the Right System: Practical Insights
Given the variables, selecting the right system involves more than just CFM numbers. Consider the space's purpose, regional climate, and potential future changes. For instance, an evenly distributed airflow is crucial in temperature-sensitive environments like data centers.
Engaging with suppliers knowledgeable in your specific industry aids in tailoring solutions to real-world needs. Partners like those found through Dahua Group can provide valuable insights and personalized advice, much beyond standard catalog specifications.
When in doubt, pilot tests in controlled areas can reveal a lot about expectations versus reality. Simple adjustments during such trials frequently preempt larger headaches post-deployment.
Reflections on Personal and Professional Experience
Each encounter with cooling systems offers lessons. The balance between technical specifications and actual conditions is delicate. I've seen first-hand how equipment like the 10000 CFM evaporative cooler can either revolutionize a space's climate or become a costly misstep.
Personal anecdotes, coupled with professional experiences, illustrate the importance of comprehensive planning and maintenance. This isn't a field for improvisation; detailed attention saves both time and resources.
Ultimately, successful evaporative cooling boils down to a blend of proper equipment selection, installation expertise, and adaptive strategies—lessons learned through industry cycles and practical engagements.
Соответствующая продукция
Соответствующая продукция
Самые продаваемые продукты
Самые продаваемые продуктыСвязанный поиск
Связанный поиск- Best FRP Ducting Manufacturer product
- OEM FRP Process Piping Price factory
- OEM FRP Pipe Fittings product
- industrial evaporative coolers for sale product
- high quality High-Alumina Bricks for Mannheim Potassium Sulfate Manufacturer
- OEM Hybrid Evaporative Cooler Manufacturer
- xerxes frp tanks product
- Best Collection Tube product
- high quality frp tank for water factory
- China Air-Cooled Heat Exchanger exit

























