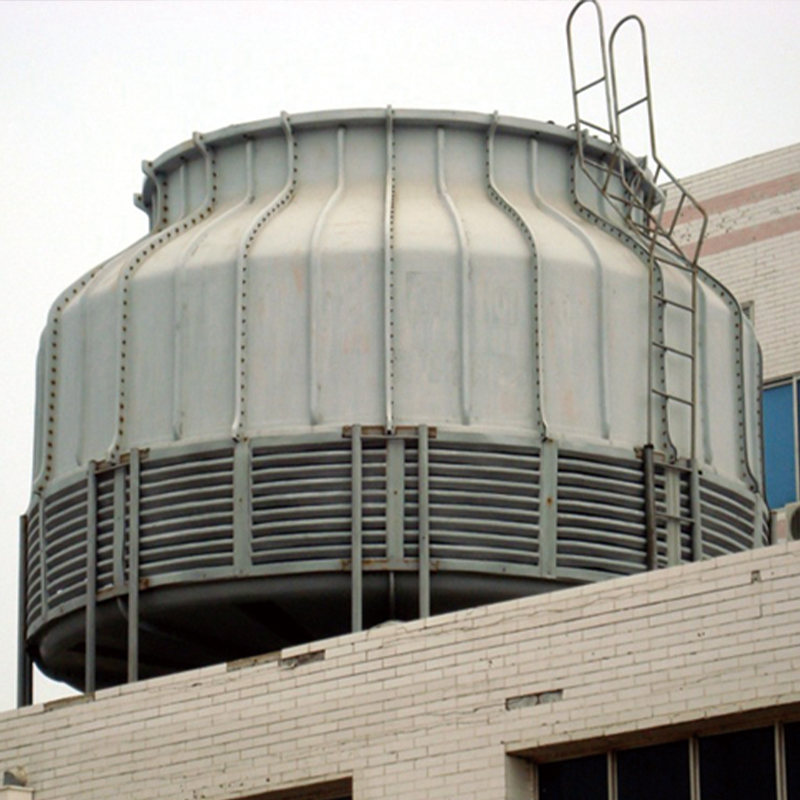

Round Counterflow Cooling Tower
The circular structure makes the flow of air inside the tower more uniform.It eliminates airflow dead zones, enabling full mechanical utilization of the tower’s internal space for highly efficient heat exchange with hot water, thereby boosting cooling efficiency.

Evaporative condenser
Based on the working principle of thermodynamic heat transfer, the evaporative condenser makes the high-temperature gaseous refrigerant in the coil exchange heat with the spray water and air outside the coil. The super wind force of the induced draft fan makes the spray water completely cover the surface of the coil, and the heat exchange effect is significantly increased by the wind force of the water. After absorbing heat spray water and air temperature, some water from liquid to gas, the latent heat of evaporation take away a lot of heat, heat the water in the air is dehydrator intercept and collected the water in the heat transfer in heat transfer layer by air cooling, temperature lowering into the sump tank, by circulating water pump to spray again continue to cycle in the system. The water evaporating into the air is automatically replenished by the control of the floating ball valve .
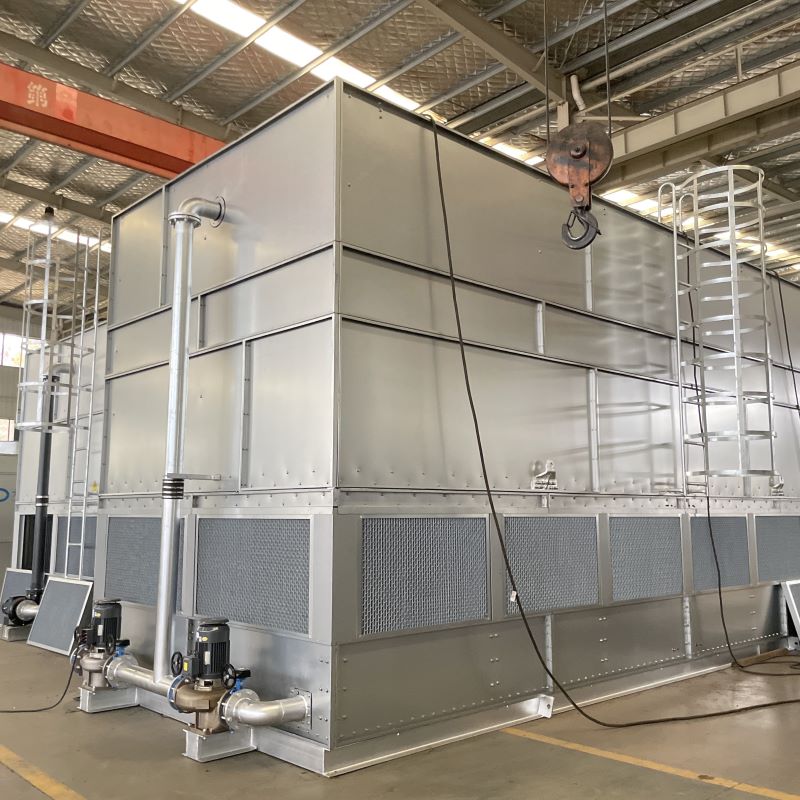

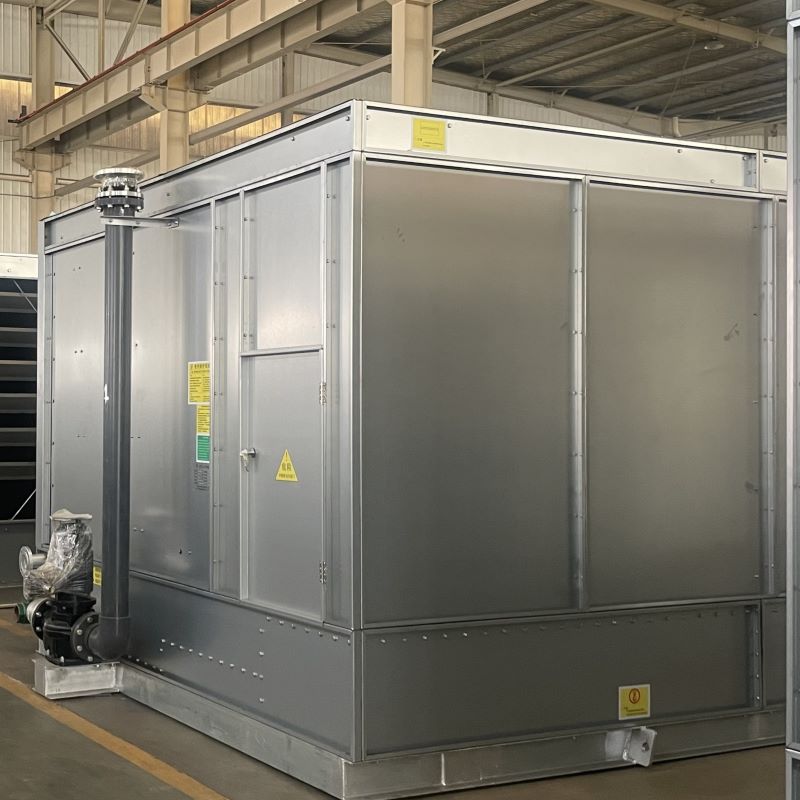
Closed Circuit Cooling Towers
The DGCC Series Tube-and-Header Type Closed Circuit Cooling Towers employ advanced latent heat transfer technology, delivering significantly higher heat exchange efficiency compared to traditional sensible heat transfer methods.Featuring a PVC-free heat exchange layer with an all-coil structure, the tower eliminates common issues associated with conventional open towers, such as packing clogging and aging.
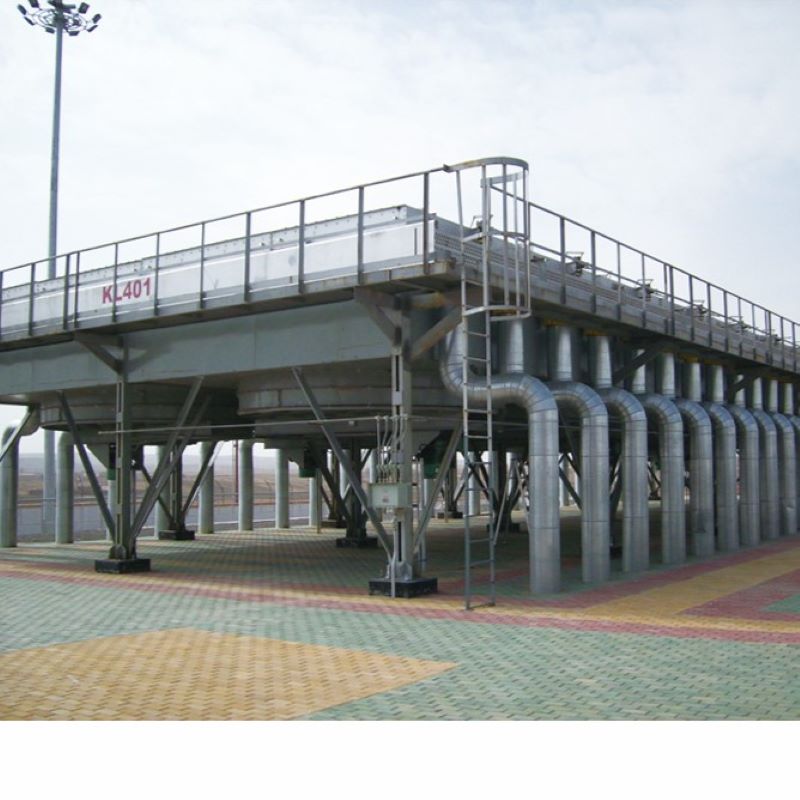

Air cooled heat exchanger
Air cooler of finned tube bundle, blower, motor, shutter and maintenance platform and frame parts, divided into drum wind, wind,inclined top three.Operation of the air cooler are cooled material through the tube, air under the action of fan, cross from outside fin tube, using the temperature difference between the two, make the high temperature material of tube cooling and condensation.
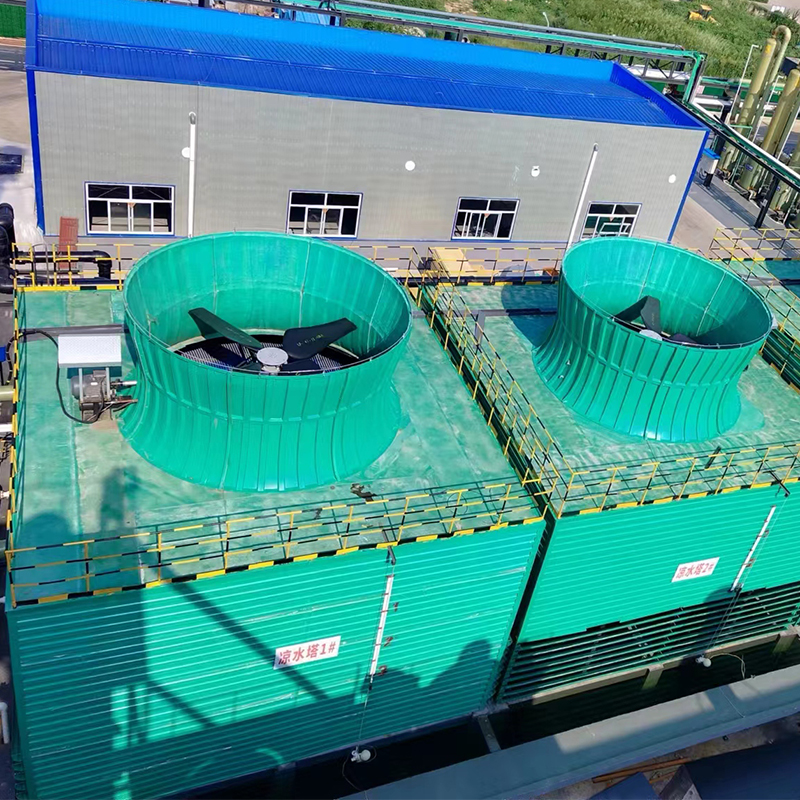

Cooling Tower
The surface of fiberglass cooling towers is smooth and can be made in various colors and shapes, which can coordinate with the surrounding environment and have good decorative properties, especially suitable for places that require environmental aesthetics.
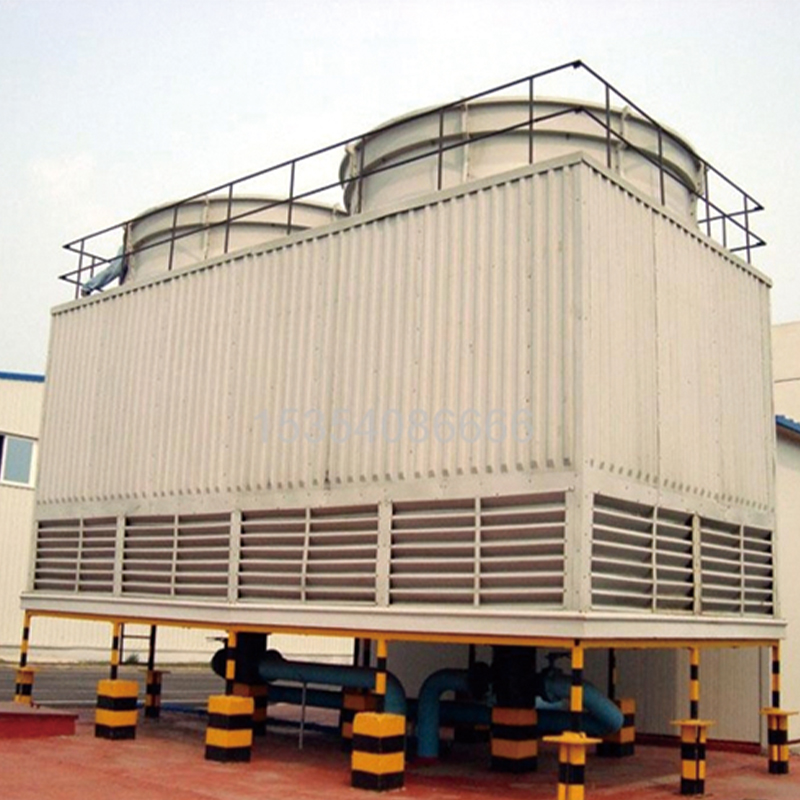

Square Counterflow Cooling Tower
It adopts the principle of counterflow cooling: hot water flows uniformly down from the top of the cooling tower, while air flows upward from the bottom of the tower, forming counterflow heat exchange. This method enables full contact between hot water and cold air, prolongs heat exchange time, and improves cooling efficiency. Compared to other cooling methods, it can more effectively reduce water temperature.
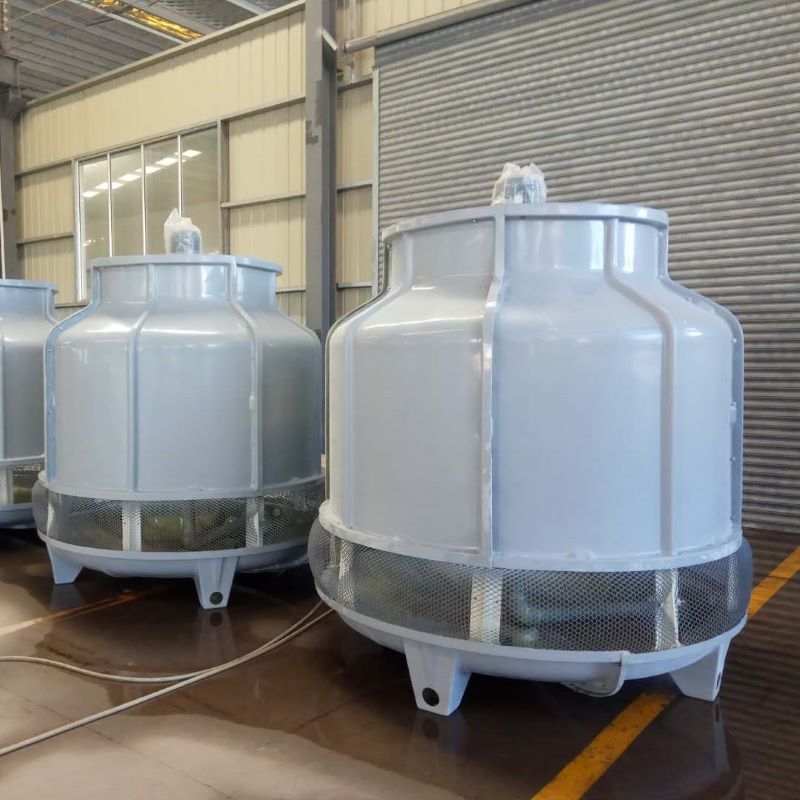

Circular cooling towers
Glass fiber reinforced plastic (FRP) cooling towers are categorized into cross-flow, counter-flow, spray-type, and non-powered types, featuring rational structural designs with concrete supporting frameworks. These FRP cooling towers demonstrate excellent cooling efficiency, low noise levels, minimal water splashing, stable performance, easy maintenance, and large circulating water capacity, making them suitable for various industrial recirculating water systems.
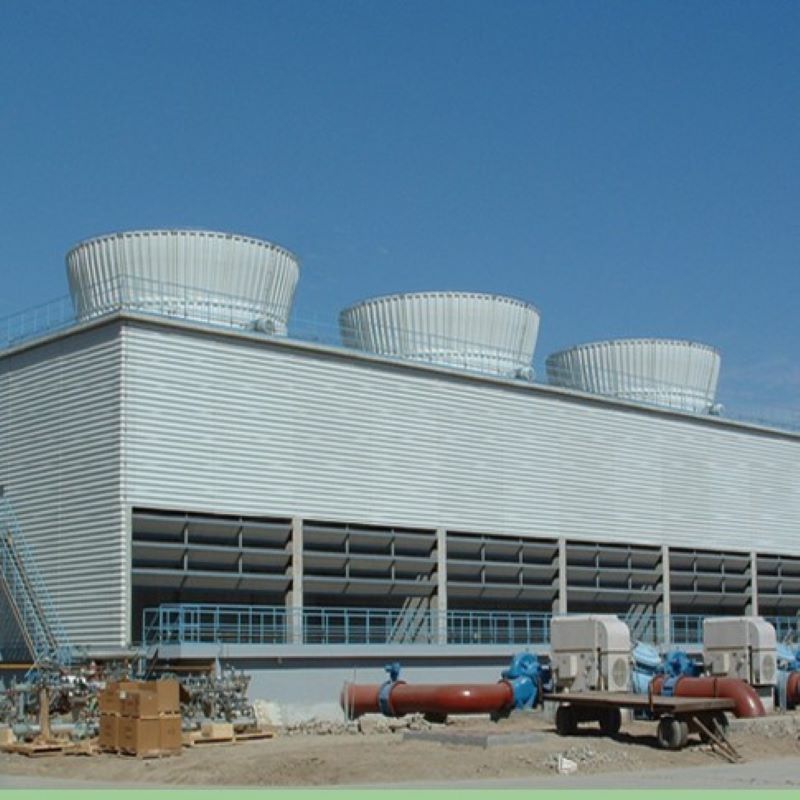

Square cooling towers
Glass fiber reinforced plastic (FRP) cooling towers are categorized into cross-flow, counter-flow, spray-type, and non-powered types, featuring rational structural designs with concrete supporting frameworks. These FRP cooling towers demonstrate excellent cooling efficiency, low noise levels, minimal water splashing, stable performance, easy maintenance, and large circulating water capacity, making them suitable for various industrial recirculating water systems.
Heat Exchange Equipment
The company's leading products include Glass Fiber Reinforced Plastic (FRP) equipment like FRP storage tanks, FRP reaction tanks, FRP pipes, FRP tower equipment and FRP cooling towers;PPH equipment like PPH storage tanks, PPH reaction tanks and PPH absorption towers.;composite evaporative condensers, high-efficiency energy-saving closed-circuit cooling towers, air coolers, and chemical/petrochemical air coolers. Additionally, we undertake Mannheim-process potassium sulfate EPC projects and calcium chloride projects.







